Home > Press > Charge density and optical properties of multicomponent crystals
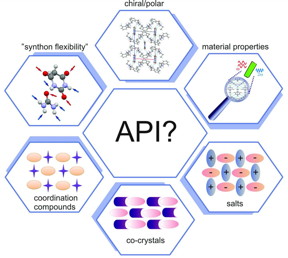 |
| APIs in the design of multi-component functional solids are shown. CREDIT: Marlena Gryl |
Abstract:
Optical materials serve a major role in modern sciences and technology. Many of the devices we use feature technology resulting from material discoveries in this fast moving area of research. Nowadays, the need for more efficient devices and minimisation in optoelectronics requires a novel approach towards crystal engineering of functional solids. A solution can be multicomponent materials built from either organic or mixed organic and inorganic components selected in a specific way, to combine molecular and structural properties to form a 3D architecture. Optical properties of a crystal strongly depend on two factors, i.e. the spatial distribution of molecules in the crystal structure and the electronic properties of molecular building blocks. The latter are easy to predict whereas the former are not. Crystal symmetry is often a key to obtaining a desired property. Noncentrosymmetric crystal structure (chiral/polar) is a necessary (limiting) condition for such properties as nonlinear properties of even order and linear properties like optical activity, piezoelectricity, pyroelectricity and ferroelectricity. However, fulfilling symmetry rules does not guarantee the existence of a physical effect. The choice of building blocks is crucial; in ideal cases, push-pull molecules should be linked with constituents enabling synthon formation flexibility.
Charge density and optical properties of multicomponent crystals
Chester, UK | Posted on August 9th, 2015Active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), through their favourable donor/acceptor spatial distribution and synthon formation flexibility, are attractive building blocks in modern materials crystallography. An API is a substance or a mixture of substances used in the manufacture of a drug product and which becomes an active ingredient in the drug product itself. Here, a Polish scientist (working in Professor Katarzyna Stadnicka's group at the Jagiellonian University in Kraków) presents design strategies for optical materials based on selected pharmaceutical molecules [Gryl (2015). Acta Cryst. B71, 392-405; doi:10.1107/S2052520615013505]. Gryl successfully presents the factors that contribute to molecular recognition in the four selected polar/chiral crystal phases. Theoretically predicted optical properties of the molecular/ionic building blocks as well as bulk effects were all confirmed experimentally. This work shows that quantitative crystal engineering techniques combining structural analysis, charge density studies, prediction of properties and their measurements enable the full analysis of the obtained functional materials in terms of their usefulness in practical applications. The study is just a first step in the design of novel optical materials based on push-pull molecules and APIs.
This work presents an alternative application for pharmaceutical solids that are of major interest in the pharmaceutical industry. Dr Gryl's journey with optical materials based on API started with three polymorphs of urea and barbituric acid adduct [Gryl, Krawczuk & Stadnicka (2008). Acta Cryst. B64, 623-632; doi:10.1107/S0108768108026645]. The co-crystals display synthon polymorphism (a possibility to use the same donor and acceptor sites in many ways) and hence enable the manipulation of the outcome of the engineering process. Why not use the same "flexible" molecules and incorporate them in a lattice containing components with high molecular (hyper)polarizability? This is a next step in Dr Gryl's research. First, of course, as much as possible needs to be known about the selected building blocks and there is no better way than to study crystal structures containing those building blocks.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Jonathan Agbenyega
44-124-434-2878
Copyright © International Union of Crystallography
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








