Home > Press > Lightning reshapes rocks at the atomic level, Penn study finds
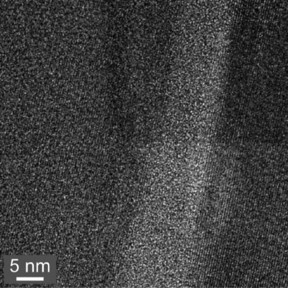 |
| Shock lamellae are formed when lightning hits rock, the study found. Here, a single lamella is seen under a transmission electron microscope. Lamellae appear as straight, parallel lines and occur when the crystal structure of a mineral deforms in response to a vast wave of pressure. CREDIT: University of Pennsylvania |
Abstract:
At a rock outcropping in southern France, a jagged fracture runs along the granite. The surface in and around the crevice is discolored black, as if wet or covered in algae. But, according to a new paper coauthored by the University of Pennsylvania's Reto Gieré, the real explanation for the rock's unusual features is more dramatic: a powerful bolt of lightning.
Lightning reshapes rocks at the atomic level, Penn study finds
Philadelphia, PA | Posted on August 5th, 2015Using extremely high-resolution microscopy, Gieré, professor and chair of the Department of Earth and Environmental Science in Penn's School of Arts & Sciences, and his coauthors found that not only had the lightning melted the rock's surface, resulting in a distinctive black "glaze," but had transferred enough pressure to deform a thin layer of quartz crystals beneath the surface, resulting in distinct atomic-level structures called shock lamellae.
Prior to this study, the only natural events known to create this type of lamellae were meteorite impacts.
"I think the most exciting thing about this study is just to see what lightning can do," Gieré said. "To see that lightning literally melts the surface of a rock and changes crystal structures, to me, is fascinating."
Gieré said the finding serves as a reminder to geologists not to rush to interpret shock lamellae as indicators of a meteorite strike.
"Most geologists are careful; they don't just use one observation," he said, "But this is a good reminder to always use multiple observations to draw big conclusions, that there are multiple mechanisms that can result in a similar effect."
Gieré collaborated on the study with Wolfhard Wimmenauer and Hiltrud Müller-Sigmund of Albert-Ludwigs-Universität, Richard Wirth of GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam and Gregory R. Lumpkin and Katherine L. Smith of the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organization.
The paper was published in the journal American Mineralogist.
Geologists have long known that lightning, through rapid increases in temperature as well as physical and chemical effects, can alter sediments. When it strikes sand, for example, lightning melts the grains, which fuse and form glass tubes known as fulgurites.
Fulgurites can also form when lightning strikes other materials, including rock and soil. The current study examined a rock fulgurite found near Les Pradals, France. Gieré and colleagues took samples from the rock, then cut thin sections and polished them.
Under an optical microscope, they found that the outer black layer -- the fulgurite itself -- appeared shiny, "almost like a ceramic glaze," Gieré said.
The layer was also porous, almost like a foam, due to the lightning's heat vaporizing the rock's surface. A chemical analysis of the fulgurite layer turned up elevated levels of sulfur dioxide and phosphorous pentoxide, which the researchers believe may have derived from lichen living on the rock's surface at the time of the lightning strike.
The team further studied the samples using a transmission electron microscope, which allows users to examine specimens at the atomic level. This revealed that the fulgurite lacked any crystalline structure, consistent with it representing a melt formed through the high heat from the lightning strike.
But, in a layer of the sample immediately adjacent to the fulgurite, slightly deeper in the rock, the researchers spotted an unusual feature: a set of straight, parallel lines known as shock lamellae. This feature occurs when the crystal structure of quartz or other minerals deform in response to a vast wave of pressure.
"It's like if someone pushes you, you rearrange your body to be comfortable," Gieré said. "The mineral does the same thing."
The lamellae were present in a layer of the rock only about three micrometers wide, indicating that the energy of the lightning bolt's impact dissipated over that distance.
This characteristic deformation of crystals had previously only been seen in minerals from sites where meteorites struck. Shock lamellae are believed to form at pressures up to more than 10 gigapascals, or with 20 million times greater force than a boxer's punch.
Gieré and colleagues hope to study rock fulgurites from other sites to understand the physical and chemical effects of lightning bolts on rocks in greater detail.
Another takeaway for geologists, rock climbers and hikers who spend time on rocks in high, exposed places is to beware when they see the tell-tale shiny black glaze of a rock fulgurite, as it might indicate a site prone to lightning strikes.
"Once it was pointed out to me, I started seeing it again and again," he said. "I've had some close calls with thunderstorms in the field, where I've had to throw down my metal instruments and run."
###
The study was supported in part by the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organization.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Katherine Unger Baillie
215-898-9194
Copyright © University of Pennsylvania
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








