Home > Press > Meet the high-performance single-molecule diode: Major milestone in molecular electronics scored by Berkeley Lab and Columbia University team
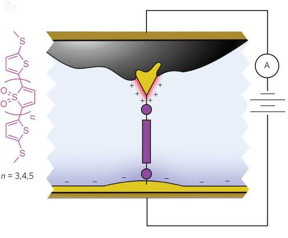 |
| Schematic of the molecular junction created using asymmetric area electrodes which functions as a diode, allowing current to flow in one direction only. CREDIT: courtesy of Berkeley Lab and Columbia University |
Abstract:
A team of researchers from Berkeley Lab and Columbia University has passed a major milestone in molecular electronics with the creation of the world's highest-performance single-molecule diode. Working at Berkeley Lab's Molecular Foundry, a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility, the team used a combination of gold electrodes and an ionic solution to create a single-molecule diode that outperforms the best of its predecessors by a factor of 50.
Meet the high-performance single-molecule diode: Major milestone in molecular electronics scored by Berkeley Lab and Columbia University team
Berkeley, CA | Posted on July 29th, 2015"Using a single symmetric molecule, an ionic solution and two gold electrodes of dramatically different exposed surface areas, we were able to create a diode that resulted in a rectification ratio, the ratio of forward to reverse current at fixed voltage, in excess of 200, which is a record for single-molecule devices," says Jeff Neaton, Director of the Molecular Foundry, a senior faculty scientist with Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division and the Department of Physics at the University of California Berkeley, and a member of the Kavli Energy Nanoscience Institute at Berkeley (Kavli ENSI).
"The asymmetry necessary for diode behavior originates with the different exposed electrode areas and the ionic solution," he says. "This leads to different electrostatic environments surrounding the two electrodes and superlative single-molecule device behavior."
With "smaller and faster" as the driving mantra of the electronics industry, single-molecule devices represent the ultimate limit in electronic miniaturization. In 1974, molecular electronics pioneers Mark Ratner and Arieh Aviram theorized that an asymmetric molecule could act as a rectifier, a one-way conductor of electric current. Since then, development of functional single-molecule electronic devices has been a major pursuit with diodes - one of the most widely used electronic components - being at the top of the list.
A typical diode consists of a silicon p-n junction between a pair of electrodes (anode and cathode) that serves as the "valve" of an electrical circuit, directing the flow of current by allowing it to pass through in only one "forward" direction. The asymmetry of a p-n junction presents the electrons with an "on/off" transport environment. Scientists have previously fashioned single-molecule diodes either through the chemical synthesis of special asymmetric molecules that are analogous to a p-n junction; or through the use of symmetric molecules with different metals as the two electrodes. However, the resulting asymmetric junctions yielded low rectification ratios, and low forward current. Neaton and his colleagues at Columbia University have discovered a way to address both deficiencies.
"Electron flow at molecular length-scales is dominated by quantum tunneling," Neaton explains. "The efficiency of the tunneling process depends intimately on the degree of alignment of the molecule's discrete energy levels with the electrode's continuous spectrum. In a molecular rectifier, this alignment is enhanced for positive voltage, leading to an increase in tunneling, and is reduced for negative voltage. At the Molecular Foundry we developed an approach to accurately compute energy-level alignment and tunneling probability in single-molecule junctions. This method allowed myself and Zhenfei Liu to understand the diode behavior quantitatively."
In collaboration with Columbia University's Latha Venkataraman and Luis Campos and their respective research groups, Neaton and Liu fabricated a high-performing rectifier from junctions made of symmetric molecules with molecular resonance in nearly perfect alignment with the Fermi electron energy levels of the gold electrodes. Symmetry was broken by a substantial difference in the size of the area on each gold electrode that was exposed to the ionic solution. Owing to the asymmetric electrode area, the ionic solution, and the junction energy level alignment, a positive voltage increases current substantially; a negative voltage suppresses it equally significantly.
"The ionic solution, combined with the asymmetry in electrode areas, allows us to control the junction's electrostatic environment simply by changing the bias polarity," Neaton says. "In addition to breaking symmetry, double layers formed by ionic solution also generate dipole differences at the two electrodes, which is the underlying reason behind the asymmetric shift of molecular resonance. The Columbia group's experiments showed that with the same molecule and electrode setup, a non-ionic solution yields no rectification at all."
The Berkeley Lab-Columbia University team believes their new approach to a single-molecule diode provides a general route for tuning nonlinear nanoscale-device phenomena that could be applied to systems beyond single-molecule junctions and two-terminal devices.
"We expect the understanding gained from this work to be applicable to ionic liquid gating in other contexts, and mechanisms to be generalized to devices fabricated from two-dimensional materials," Neaton says. "Beyond devices, these tiny molecular circuits are petri dishes for revealing and designing new routes to charge and energy flow at the nanoscale. What is exciting to me about this field is its multidisciplinary nature - the need for both physics and chemistry - and the strong beneficial coupling between experiment and theory.
"With the increasing level of experimental control at the single-molecule level, and improvements in theoretical understanding and computational speed and accuracy, we're just at the tip of the iceberg with what we can understand and control at these small length scales."
Neaton, Venkataraman and Campos are the corresponding authors of a paper describing this research in Nature Nanotechnology. The paper is titled "Single-molecule diodes with high rectification ratios through environmental control." Other co-authors are Brian Capozzi, Jianlong Xia, Olgun Adak, Emma Dell, Zhen-Fei Liu and Jeffrey Taylor.
###
This research was primarily supported by the DOE Office of Science and the National Science Foundation. Portions of the computation work were performed at National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center (NERSC), a DOE Office of Science User Facility also hosted at Berkeley Lab.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Lynn Yarris
510-486-5375
Copyright © DOE/Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








