Home > Press > Researchers grind nanotubes to get nanoribbons: Rice-led experiments demonstrate solid-state carbon nanotube 'templates'
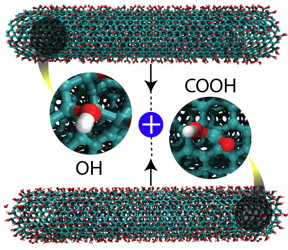 |
| Researchers led by materials scientists at Rice University discovered that altering carbon nanotubes with carboxyl (COOH) and hydroxyl (OH) groups and grinding them together produces nanoribbons. The find could lead to novel nanostructured products with specific properties. Credit: Mohamad Kabbani/Rice University |
Abstract:
A simple way to turn carbon nanotubes into valuable graphene nanoribbons may be to grind them, according to research led by Rice University.
Researchers grind nanotubes to get nanoribbons: Rice-led experiments demonstrate solid-state carbon nanotube 'templates'
Houston, TX | Posted on June 15th, 2015The trick, said Rice materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan, is to mix two types of chemically modified nanotubes. When they come into contact during grinding, they react and unzip, a process that until now has depended largely on reactions in harsh chemical solutions.
The research by Ajayan and his international collaborators appears in Nature Communications.
To be clear, Ajayan said, the new process is still a chemical reaction that depends on molecules purposely attached to the nanotubes, a process called functionalization. The most interesting part to the researchers is that a process as simple as grinding could deliver strong chemical coupling between solid nanostructures and produce novel forms of nanostructured products with specific properties.
"Chemical reactions can easily be done in solutions, but this work is entirely solid state," he said. "Our question is this: If we can use nanotubes as templates, functionalize them and get reactions under the right conditions, what kinds of things can we make with a large number of possible nanostructures and chemical functional groups?"
The process should enable many new chemical reactions and products, said Mohamad Kabbani, a graduate student at Rice and lead author of the paper. "Using different functionalities in different nanoscale systems could revolutionize nanomaterials development," he said.
Highly conductive graphene nanoribbons, thousands of times smaller than a human hair, are finding their way into the marketplace in composite materials. The nanoribbons boost the materials' electronic properties and/or strength.
"Controlling such structures by mechano-chemical transformation will be the key to find new applications," said co-author Thalappil Pradeep, a professor of chemistry at the Indian Institute of Technology Chennai. "Soft chemistry of this kind can happen in many conditions, contributing to better understanding of materials processing."
In their tests, the researchers prepared two batches of multi-walled carbon nanotubes, one with carboxyl groups and the other with hydroxyl groups attached. When ground together for up to 20 minutes with a mortar and pestle, the chemical additives reacted with each other, triggering the nanotubes to unzip into nanoribbons, with water as a byproduct.
"That serendipitous observation will lead to further systematic studies of nanotubes reactions in solid state, including ab-initio theoretical models and simulations," Ajayan said. "This is exciting."
The experiments were duplicated by participating labs at Rice, at the Indian Institute of Technology and at the Lebanese American University in Beirut. They were performed in standard lab conditions as well as in a vacuum, outside in the open air and at variable humidity, temperatures, times and seasons.
The researchers who carried out the collaboration on three continents still don't know precisely what's happening at the nanoscale. "It is an exothermic reaction, so the energy's enough to break up the nanotubes into ribbons, but the details of the dynamics are difficult to monitor," Kabbani said. "There's no way we can grind two nanotubes in a microscope and watch it happen. Not yet, anyway."
But the results speak for themselves.
"I don't know why people haven't explored this idea, that you can control reactions by supporting the reactants on nanostructures," Ajayan said. "What we've done is very crude, but it's a beginning and a lot of work can follow along these lines."
Co-authors are Rice graduate students Chandra Sekhar Tiwary, Sehmus Ozden and Yongji Gong; Pedro Autreto, Gustavo Brunetto and Professor Douglas Galvao of the State University of Campinas, Brazil; Anirban Som and K.R. Krishnadas of the Indian Institute of Technology Madras; Robert Vajtai, a senior faculty fellow at Rice, and Ahmad Kabbani, an adjunct faculty member at Rice and a professor of chemistry at the Lebanese American University, Beirut. Ajayan is chair of Rice's Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering, the Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Engineering and a professor of chemistry.
The research was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and its Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative; the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, CAPES (Coordination of Improvement of Higher Education Personnel) and the São Paulo Research Foundation; the Center for Computational Engineering and Sciences at the State University of Campinas, and the Nano Mission, Government of India.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,888 undergraduates and 2,610 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked among some of the top schools for best quality of life by the Princeton Review and for best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
Rice Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








