Home > Press > Framework materials yield to pressure
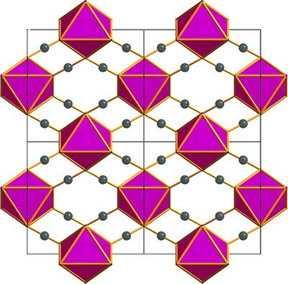 |
| This is a cobalt II octahedral packing diagram as viewed in the (001) plane.
CREDIT: Yakovenko et al |
Abstract:
Pressure is a powerful thermodynamic variable that enables the structure, bonding and reactivity of matter to be altered. In materials science it has become an indispensable research tool in the quest for novel functional materials.
Framework materials yield to pressure
Chester, UK | Posted on June 11th, 2015Materials scientists can exploit the effectiveness of pressure for probing and tuning structural, mechanical, electronic, magnetic and vibrational properties of materials in situ; crystallography plays a crucial role, enabling on the one hand the unravelling of structural phenomena through a better understanding of interactions, and on the other shedding light on the correlation of structure and properties [Fabbiani (2015), Acta Cryst. B71, 247-249; doi: 10.1107/S2052520615009427].
With high pressure promoting effects such as magnetic crossover, spin transitions, negative linear compressibility, changes in proton conductivity, or even phase transitions that generate porous structures, high-pressure crystallographic studies on dense framework materials are on the rise. More generally, coordination compounds are a fascinating class of materials for high-pressure crystallographic studies, compared with purely organic compounds; they have an inherent extra degree of flexibility for responding to moderate applied pressures, as the geometry at the metal centre can undergo marked changes, whereas other primary bond distances and angles remain largely unaffected.
A group of scientists [Yakovenko et al. (2015), Acta Cryst. B71, 252-257; doi: 10.1107/S2052520615005867] demonstrate that pressure offers a novel approach for generating new phases and exploring the structure-property relationships of molecular materials.
In their study the researchers present a high-pressure crystallographic study of α -Co(dca)2, including the structural determination of the high-pressure phase γ -Co(dca)2. The pressure-dependence of the atomic structure was probed within a diamond-anvil cell using synchrotron-based powder diffraction methods.
Future work from the group based at Argonne National Laboratory will involve investigations of the pressure-dependent structures of further transition metal dicyanamides, including members of the iso-structural α-MII(dca)2 family as well as other polymorphs, to uncover any universality or metal-ion dependence associated with the α?γ transition, and if other new phases can be generated.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Jonathan Agbenyega
44-124-434-2878
Copyright © International Union of Crystallography
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Download article doi: 10.1107/S2052520615009427:
Download article doi: 10.1107/S2052520615009427:
![]() Download article doi: 10.1107/S2052520615005867:
Download article doi: 10.1107/S2052520615005867:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Alliances/Trade associations/Partnerships/Distributorships
![]() Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
Chicago Quantum Exchange welcomes six new partners highlighting quantum technology solutions, from Chicago and beyond September 23rd, 2022
![]() University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
University of Illinois Chicago joins Brookhaven Lab's Quantum Center June 10th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








