Home > Press > New technique speeds nanoMRI imaging: Multiplexing technique for nanoscale magnetic resonance imaging developed by researchers in Switzerland cuts normal scan time from two weeks to two days
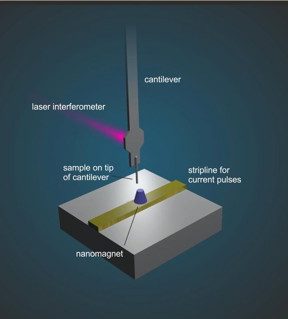 |
| Basic principles of magnetic resonance force microscopy. CREDIT: B.A. Moores |
Abstract:
NanoMRI is a scanning technique that produces nondestructive, high-resolution 3-D images of nanoscale objects, and it promises to become a powerful tool for researchers and companies exploring the shape and function of biological materials such as viruses and cells in much the same way as clinical MRI today enables investigation of whole tissues in the human body.
New technique speeds nanoMRI imaging: Multiplexing technique for nanoscale magnetic resonance imaging developed by researchers in Switzerland cuts normal scan time from two weeks to two days
Washington, DC | Posted on May 28th, 2015Producing images with near-atomic resolution, however, is immensely difficult and time-consuming. A single nanoMRI scan can require weeks to complete.
Striving to overcome this limitation, researchers from ETH Zurich in Switzerland developed a parallel measurement technique, which they report in a paper appearing this week on the cover of the journal Applied Physics Letters, from AIP Publishing. Information that normally would be measured sequentially -- one bit after another -- can now be measured at the same time with a single detector.
"As a loose analogy, think of how your eyes register green, red, and blue information at the same time using different receptors -- you're measuring different colors in parallel," said Alexander Eichler, a postdoctoral researcher and teaching assistant in Professor C. Degen's group within the Department of Physics at ETH Zurich.
Parallel measurement is also referred to as "multiplexing." After the scan, the researchers need to be able to distinguish where each bit of information belongs in the final picture. For this reason, "different bits of information are encoded in the detector using different phases," he explained. "The term 'phase' refers to a lag in a periodic signal. The phase can be used to differentiate between periodic signals in a way similar to how color is used to differentiate between light signals in the eye."
Magnetic resonance imaging makes use of the fact that certain atoms -- such as 1H, 13C, or 19F -- have nuclei that act like tiny spinning magnets. When these atoms are brought into a magnetic field, they rotate around the field axis in much the same way a spinning top rotates around its vertical axis when it isn't perfectly balanced.
"This rotation is called 'precession,' and it happens at a very precise frequency, known as the 'Larmor frequency,' which depends on the field strength and type of atom," said Eichler.
In a nonhomogeneous field, atoms at different locations have different Larmor frequencies. The atom's location "can be evaluated from the frequency at which it precesses, and an image of the location of all atoms can be composed," he added. "When you look at a clinical MRI picture, you see bright pixels where the density of atoms -- typically 1H -- is high, and dark pixels where the density is low."
The magnetic strength of a single atom is vanishingly small. "Clinical MRI is only possible because a single 3-D pixel -- a "voxel" -- contains about 1018 atoms," Eichler pointed out. "With nanoMRI, we want to detect voxels with only a thousand atoms or less, meaning that we need a sensitivity at least a quadrillion [10^15, or a million billion] times better."
To achieve this, various strategies have been developed. The research team working with Professor Degen demonstrated phase multiplexing with a particular nanoMRI technique called "magnetic resonance force microscopy" (MRFM), in which the atomic nuclei experience a tiny magnetic force that's transferred to a cantilever acting as a mechanical detector. In response to the magnetic force, the cantilever vibrates and then, in turn, an image can be assembled from the measured vibration.
"Our research overcomes one of the major obstacles toward practical high-resolution nanoMRI, namely the forbidding time scales required for sequential measurements," Eichler said. "It brings us closer to the commercial implementation of nanoMRI."
In other words, the team's work greatly accelerates the speed of nanoMRI measurements. By demonstrating parallel measurements of six data points, they've shown that a normal scan of two weeks can now be compressed to within two days.
"Acceleration is limited by technical issues such as the speed of spin reversal and the stability of phase-sensitive detection," Eichler noted. "But, in principle, phase multiplexing might allow compression rates of ten or more. With commercial applications in mind, this time gain is crucial because it makes a huge difference to a pharmaceutical company if a virus can be characterized within three days rather than a month."
Next, the researchers at ETH Zurich are turning their focus to nanoMRI measurements of biological systems. In particular, they'd "like to demonstrate a spatial resolution of better than 1 nanometer," Eichler said. "Taking into account that the number of atoms in a voxel scales with the cube of the length, this will require an improvement in sensitivity of more than 100 relative to prior work -- the current record resolution is about 5 nanometers."
The preparation of biological objects for low-temperature, high-vacuum measurements is a particular challenge, because an ordinary cell, if transferred into vacuum, will simply burst from the pressure imbalance. "When the cell is cooled below the freezing point of water, the liquid inside it may crystallize and destroy the cell membrane," he added. "We're developing strategies to avoid these issues so that we can transfer cells or viruses into our measurement setup without damaging them."
####
About American Institute of Physics
Applied Physics Letters features concise, rapid reports on significant new findings in applied physics. The journal covers new experimental and theoretical research on applications of physics phenomena related to all branches of science, engineering, and modern technology. See: apl.aip.org
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jason Socrates Bardi
240-535-4954
Copyright © American Institute of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








