Home > Press > Engineering Phase Changes in Nanoparticle Arrays: Scientists alter attractive and repulsive forces between DNA-linked particles to make dynamic, phase-shifting forms of nanomaterials
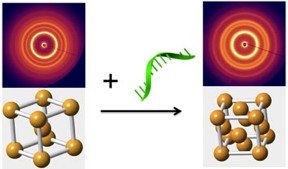 |
| Introducing "reprogramming" DNA strands into an already assembled nanoparticle array triggers a transition from a "mother phase," where particles occupy the corners and center of a cube (left), to a more compact "daughter phase" (right). The change represented in the schematic diagrams is revealed by the associated small-angle x-ray scattering patterns. Such phase-changes could potentially be used to switch a material's properties on demand. |
Abstract:
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory have just taken a big step toward the goal of engineering dynamic nanomaterials whose structure and associated properties can be switched on demand. In a paper appearing in Nature Materials, they describe a way to selectively rearrange the nanoparticles in three-dimensional arrays to produce different configurations, or phases, from the same nano-components.
Engineering Phase Changes in Nanoparticle Arrays: Scientists alter attractive and repulsive forces between DNA-linked particles to make dynamic, phase-shifting forms of nanomaterials
Upton, NY | Posted on May 25th, 2015"One of the goals in nanoparticle self-assembly has been to create structures by design," said Oleg Gang, who led the work at Brookhaven's Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN, www.bnl.gov/cfn/), a DOE Office of Science User Facility. "Until now, most of the structures we've built have been static. Now we are trying to achieve an even more ambitious goal: making materials that can transform so we can take advantage of properties that emerge with the particles' rearrangements."
The ability to direct particle rearrangements, or phase changes, will allow the scientists to choose the desired properties-say, the material's response to light or a magnetic field-and switch them as needed. Such phase-changing materials could lead to new applications, such as dynamic energy-harvesting or responsive optical materials.
DNA-directed rearrangement
This latest advance in nanoscale engineering builds on the team's previous work developing ways to get nanoparticles to self-assemble into complex composite arrays, including linking them together with tethers constructed of complementary strands of synthetic DNA. In this case, they started with an assembly of nanoparticles already linked in a regular array by the complementary binding of the A, T, G, and C bases on single stranded DNA tethers, then added "reprogramming" DNA strands to alter the interparticle interactions.
"We know that properties of materials built from nanoparticles are strongly dependent on their arrangements," said Gang. "Previously, we've even been able to manipulate optical properties by shortening or lengthening the DNA tethers. But that approach does not permit us to achieve a global reorganization of the entire structure once it's already built."
In the new approach, the reprogramming DNA strands adhere to open binding sites on the already assembled nanoparticles. These strands exert additional forces on the linked-up nanoparticles.
"By introducing different types of reprogramming DNA strands, we modify the DNA shells surrounding the nanoparticles," explained CFN postdoctoral fellow Yugang Zhang, the lead author on the paper. "Altering these shells can selectively shift the particle-particle interactions, either by increasing both attraction and repulsion, or by separately increasing only attraction or only repulsion. These reprogrammed interactions impose new constraints on the particles, forcing them to achieve a new structural organization to satisfy those constraints."
Using their method, the team demonstrated that they could switch their original nanoparticle array, the "mother" phase, into multiple different daughter phases with precision control.
This is quite different from phase changes driven by external physical conditions such as pressure or temperature, Gang said, which typically result in single phase shifts, or sometimes sequential ones. "In those cases, to go from phase A to phase C, you first have to shift from A to B and then B to C," said Gang. "Our method allows us to pick which daughter phase we want and go right to that one because the daughter phase is completely determined by the type of DNA reprogramming strands we use."
The scientists were able to observe the structural transformations to various daughter phases using a technique called in situ small-angle x-ray scattering at the National Synchrotron Light Source (http://www.bnl.gov/ps/), another DOE Office of Science User Facility that operated at Brookhaven Lab from 1982 until last September (now replaced by NSLS-II, which produces x-ray beams 10,000 times brighter). The team also used computational modeling to calculate how different kinds of reprogramming strands would alter the interparticle interactions, and found their calculations agreed well with their experimental observations.
"The ability to dynamically switch the phase of an entire superlattice array will allow the creation of reprogrammable and switchable materials wherein multiple, different functions can be activated on demand," said Gang. "Our experimental work and accompanying theoretical analysis confirm that reprogramming DNA-mediated interactions among nanoparticles is a viable way to achieve this goal."
This was done in collaboration with scientists from Columbia University's School of Engineering and Applied Science and the Indian Institute of Technology Gandhinagar. The work was funded by the DOE Office of Science.
####
About Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
One of ten national laboratories overseen and primarily funded by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Brookhaven National Laboratory conducts research in the physical, biomedical, and environmental sciences, as well as in energy technologies and national security. Brookhaven Lab also builds and operates major scientific facilities available to university, industry and government researchers. Brookhaven is operated and managed for DOE's Office of Science by Brookhaven Science Associates, a limited-liability company founded by the Research Foundation for the State University of New York on behalf of Stony Brook University, the largest academic user of Laboratory facilities, and Battelle, a nonprofit applied science and technology organization.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Karen McNulty Walsh
(631) 344-8350
or
Peter Genzer
(631) 344-3174
Copyright © Brookhaven National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








