Home > Press > Studying dynamics of ion channels
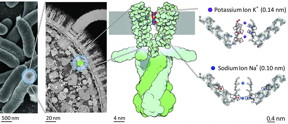 |
| Location of the potassium channel KcsA in the cell membrane of bacteria. The schematic illustration on the right shows the changes in strength and direction of vibrational coupling inside the filter depending on the ion species, as found by the study. CREDIT: Copyright: David S. Goodsell & RCSB Protein Data Bank |
Abstract:
Ion channels are essential structures of life. Ion channels are specialized pores in the cell membrane and move charged atoms known as ions in and out of cells, thereby controlling a wide variety of biological processes including brain function and heartbeat. Ion channels are generally selective for certain ions, allowing specific types of ions to flow through at very high rates, while hindering the flow of others. On the basis of this selective permeability, ion channels are classified as potassium channels, sodium channels, etc.
Studying dynamics of ion channels
Vienna, Austria | Posted on May 18th, 2015The cell's most ubiquitous gateways are potassium ion channels - the importance of this type of ion channels was underpinned in 2003 when Roderick MacKinnon received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for resolving the first atomic structure of the bacterial KcsA potassium channel.
Despite a large body of work, the exact molecular details underlying ion selectivity and transport of the potassium channel remain unclear. "Since conventional methods, such as X-ray crystallography, capture only averaged frozen structures, it is not possible to investigate how the dynamic of the protein could be involved in key aspects of their function", explains physicist Alipasha Vaziri, a joint group leader at the Max F. Perutz Laboratories (MFPL) and the Institute of Molecular Pathology (IMP) and head of the research platform "Quantum Phenomena & Nanoscale Biological Systems" (QuNaBioS) of the University of Vienna.
New method to unravel the secret of ion channel selectivity
Vaziri's team, together with researchers at the Institute for Biophysical Dynamics (University of Chicago), have now used infrared (IR) spectroscopy coupled with molecular dynamic-based simulations of the obtained spectra to investigate the subtlest changes in the shape of the KcsA potassium channel that are induced by binding either potassium or the only 0.04 nanometers smaller sodium ion. This combination proved to be a powerful tool to disentangle convoluted IR spectra - which contain contributions from the whole protein - by assigning each part of the spectrum to the amino acids that contribute to it.
"This new approach allows us to probe these mechanisms in a non perturbative way, meaning without tedious and expensive isotope labeling strategies. Moreover, it opens the way to study the structure and dynamics of ion channels on their biologically relevant timescales by extending it to two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy", says Christoph Götz, PhD student in the Vaziri lab and co-author of the paper.
The study shows for the first time that the combination of the two methods can be used to detect subtle conformational changes in large membrane proteins, such as the KcsA potassium channel. Furthermore, it opens the way to capture the dynamics of proteins in real time at atomic resolution, which has been impossible with standard techniques until now.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alipasha Vaziri
43-179-730-3540
Copyright © University of Vienna
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








