Home > Press > Gel filled with nanosponges cleans up MRSA infections
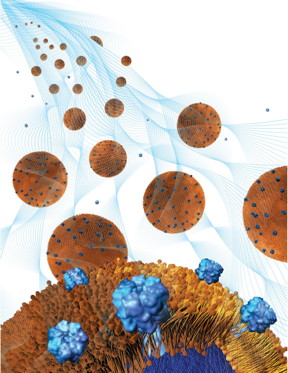 |
| Toxin-absorbing nanoparticles are loaded into a holding gel to make a nanosponge-hydrogel, which can potentially treat local bacterial infections. CREDIT: Weiwei Gao/Jacobs School of Engineering/UC San Diego |
Abstract:
Nanoengineers at the University of California, San Diego developed a gel filled with toxin-absorbing nanosponges that could lead to an effective treatment for skin and wound infections caused by MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus), an antibiotic-resistant bacteria. This "nanosponge-hydrogel" minimized the growth of skin lesions on mice infected with MRSA - without the use of antibiotics. The researchers recently published their findings online in Advanced Materials.
Gel filled with nanosponges cleans up MRSA infections
San Diego, CA | Posted on May 17th, 2015To make the nanosponge-hydrogel, the team mixed nanosponges, which are nanoparticles that absorb dangerous toxins produced by MRSA, E. coli and other antibiotic-resistant bacteria, into a hydrogel, which is a gel made of water and polymers. The hydrogel holds the nanosponges in place so that they can remove toxins at the infected spot.
"We combined the strengths of two different materials - nanosponges and hydrogels - to create a powerful formulation to treat local bacterial infections," said Liangfang Zhang, nanoengineering professor in the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego, who led the team. "Nanosponges alone are difficult to use on local tissues because they diffuse away to other parts of the body very quickly. By integrating the nanosponges into a hydrogel, we can retain them at the site of infection."
Since the nanosponge-hydrogel treatment does not involve antibiotics, the researchers say that it will not likely be affected by existing bacterial antibiotic resistance. Also, because antibiotics are not involved, the treatment will likely not cause bacteria to develop new resistance.
This work is a follow-up to a study that the team presented in Nature Nanotechnology in 2013. The previous study showed that nanosponges absorbed harmful bacterial toxins in the bloodstream and drew them away from their real targets: red blood cells. In this new study, the team reports that removing bacterial toxins could potentially lead to clearing up antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections.
"One way to treat these infections is to remove the toxins, which act as a weapon and a defense shield for the bacteria that produce them," said Zhang. "We hypothesize that without the toxins, the bacteria become significantly weakened and exposed, allowing the body's immune system to kill them more easily without the use of drugs."
Nanosponge-hydrogel treatment
How does the nanosponge-hydrogel treatment work? Each nanosponge is a nanoparticle coated in a red blood cell membrane. This coating disguises the nanosponges as red blood cells, which are the real targets of the harmful toxins produced by MRSA. By masquerading as red blood cells, the nanosponges attract harmful toxins and remove them from the bloodstream. In order for the nanosponges to remove toxins from a specific spot, such as an infected skin wound, a lot of them need to be held at that spot. This is where the hydrogel plays a role; it can hold billions of nanosponges per milliliter in one spot. The hydrogel's pores are also small enough to keep most of the nanosponges from escaping, but big enough so that toxins can easily get inside and attach to the nanosponges.
The researchers showed that the nanosponge-hydrogel treatment kept down the size of skin lesions caused by MRSA infections. In mice, the skin lesions that were treated with the nanosponge-hydrogel were significantly smaller than those that were left untreated.
"After injecting the nanosponge-hydrogel at the infected spot, we observed that it absorbed the toxins secreted by the bacteria and prevented further damage to the local blood, skin and muscle tissues," said Zhang.
The team also showed that the hydrogel was effective at holding the nanosponges in place within the body. Two days after the nanosponge-hydrogel was injected underneath the skin of a mouse, nearly 80 percent of the nanosponges were still found at the injection site. When nanosponges were injected without the hydrogel, only 20 percent of them remained at the injection site after two hours. Most of them diffused to the surrounding tissues.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Liezel Labios
858-246-1124
Copyright © University of California - San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Hydrogels
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
![]() Shrinking hydrogels enlarge nanofabrication options: Researchers from Pittsburgh and Hong Kong print intricate, 2D and 3D patterns December 29th, 2022
Shrinking hydrogels enlarge nanofabrication options: Researchers from Pittsburgh and Hong Kong print intricate, 2D and 3D patterns December 29th, 2022
![]() The deformation of the hydrogel is used to measure the negative pressure of water April 22nd, 2022
The deformation of the hydrogel is used to measure the negative pressure of water April 22nd, 2022
![]() Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
Nanocellulose decorated with proteins is suitable for 3D cell culturing September 24th, 2021
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








