Home > Press > New shortcut to solar cells: Rice University discovery employs electrodes as catalysts to make black silicon
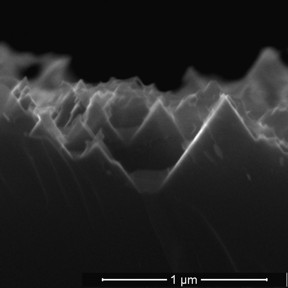 |
| An electron microscope image from earlier research shows the nanoscale spikes that make up the surface of black silicon used in solar cells.>BR> CREDIT: Barron Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
Rice University scientists have found a way to simplify the manufacture of solar cells by using the top electrode as the catalyst that turns plain silicon into valuable black silicon.
New shortcut to solar cells: Rice University discovery employs electrodes as catalysts to make black silicon
Houston, TX | Posted on May 13th, 2015The Rice lab of chemist Andrew Barron disclosed the research in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces.
Black silicon is silicon with a highly textured surface of nanoscale spikes or pores that are smaller than the wavelength of light. The texture allows the efficient collection of light from any angle, at any time of day. Barron and his team have been fine-tuning the creation of black silicon for some time, but an advance in the manufacturing technique should push it closer to commercialization, he said.
Barron noted the new work led by Rice postdoctoral researcher Yen-Tien Lu has two major attractions. "One, removing steps from the process is always good," he said. "Two, this is the first time in which metallization is a catalyst for a reaction that occurs several millimeters away."
Barron said the metal layer used as a top electrode is usually applied last in solar cell manufacturing. The new method known as contact-assisted chemical etching applies the set of thin gold lines that serve as the electrode earlier in the process, which also eliminates the need to remove used catalyst particles.
The researchers discovered that etching in a chemical bath takes place a set distance from the lines. That distance, Barron said, appears to be connected to the silicon's semiconducting properties.
"Yen-Tien was doing the reaction with gold top contacts, adding silver or gold catalyst and getting these beautiful pictures," he said. "And I said, 'OK, fine. Now let's do it without the catalysts.' Suddenly, we got black silicon -- but it was etching only a certain distance away from the contact. And no matter what we did, there was always that distance.
"It told us the electrochemical reaction is occurring at the metal contact and at the silicon that's a certain distance away," Barron said. "The distance is dependent upon the charge-carrying capacity, the conductivity, of the silicon. At some point, the conductivity isn't sufficient for the charge to carry any further."
Barron said an extremely thin layer of gold atop titanium, which bonds well with both gold and silicon, should be an effective electrode that also serves for catalysis. "The trick is to etch the valleys deep enough to eliminate the reflection of sunlight while not going so deep that you cause a short circuit in the cell," he said.
He said the electrode's ability to act as a catalyst suggests other electronic manufacturing processes may benefit from a bit of shuffling.
"Metal contacts are normally put down last," Barron said. "It begs the question for a lot of processes of whether to put the contact down earlier and use it to do the chemistry for the rest of the process."
###
The research was supported by the Robert A. Welch Foundation, the Welsh Government SÍr Cymru Programme and Natcore Technology.
Barron is the Charles W. Duncan Jr.-Welch Professor of Chemistry and a professor of materials science and nanoengineering at Rice and the SÍr Cymru Chair of Low Carbon Energy and Environment at Swansea University.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,888 undergraduates and 2,610 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked among some of the top schools for best quality of life by the Princeton Review and for best value among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() This news release can be found online at:
This news release can be found online at:
![]() Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
Wiess School of Natural Sciences:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








