Home > Press > NIST tightens the bounds on the quantum information 'speed limit'
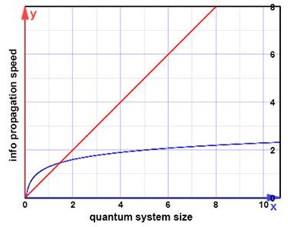 |
| The size of a quantum computer affects how quickly information can be distributed throughout it. The relation was thought to be logarithmic (blue). Progressively larger systems would need only a little more time. New findings suggest instead a power law relationship (red), meaning that the "speed limit" for quantum information transfer is far slower than previously believed.
CREDIT: NIST |
Abstract:
If you're designing a new computer, you want it to solve problems as fast as possible. Just how fast is possible is an open question when it comes to quantum computers, but physicists at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have narrowed the theoretical limits for where that "speed limit" is. The research implies that quantum processors will work more slowly than some research has suggested.*
NIST tightens the bounds on the quantum information 'speed limit'
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on April 13th, 2015The work offers a better description of how quickly information can travel within a system built of quantum particles such as a group of individual atoms. Engineers will need to know this to build quantum computers, which will have vastly different designs and be able to solve certain problems much more easily than the computers of today. While the new finding does not give an exact speed for how fast information will be able to travel in these as-yet-unbuilt computers--a longstanding question--it does place a far tighter constraint on where this speed limit could be.
Quantum computers will store data in a particle's quantum states--one of which is its spin, the property that confers magnetism. A quantum processor could suspend many particles in space in close proximity, and computing would involve moving data from particle to particle. Just as one magnet affects another, the spin of one particle influences its neighbor's, making quantum data transfer possible, but a big question is just how fast this influence can work.
The NIST team's findings advance a line of research that stretches back to the 1970s, when scientists discovered a limit on how quickly information could travel if a suspended particle only could communicate directly with its next-door neighbors. Since then, technology advanced to the point where scientists could investigate whether a particle might directly influence others that are more distant, a potential advantage. By 2005, theoretical studies incorporating this idea had increased the speed limit dramatically.
"Those results implied a quantum computer might be able to operate really fast, much faster than anyone had thought possible," says NIST's Michael Foss-Feig. "But over the next decade, no one saw any evidence that the information could actually travel that quickly."
Physicists exploring this aspect of the quantum world often line up several particles and watch how fast changing the spin of the first particle affects the one farthest down the line--a bit like standing up a row of dominoes and knocking the first one down to see how fast the chain reaction takes. The team looked at years of others' research and, because the dominoes never seemed to fall as fast as the 2005 prediction suggested, they developed a new mathematical proof that reveals a much tighter limit on how fast quantum information can propagate.
"The tighter a constraint we have, the better, because it means we'll have more realistic expectations of what quantum computers can do," says Foss-Feig.
The limit, their proof indicates, is far closer to the speed limits suggested by the 1970s result.
The proof addresses the rate at which entanglement propagates across quantum systems. Entanglement--the weird linkage of quantum information between two distant particles--is important, because the more quickly particles grow entangled with one another, the faster they can share data. The 2005 results indicated that even if the interaction strength decays quickly with distance, as a system grows, the time needed for entanglement to propagate through it grows only logarithmically with its size, implying that a system could get entangled very quickly. The team's work, however, shows that propagation time grows as a power of its size, meaning that while quantum computers may be able to solve problems that ordinary computers find devilishly complex, their processors will not be speed demons.
"On the other hand, the findings tell us something important about how entanglement works," says Foss-Feig. "They could help us understand how to model quantum systems more efficiently."
###
* M. Foss-Feig, Z.-X. Gong, C.W. Clark and A.V. Gorshkov. Nearly linear light cones in long-range interacting quantum systems. Phys. Rev. Letters, April 13, 2015.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Chad Boutin
301-975-4261
Copyright © NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF STANDARDS AND TECHNOLOGY (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








