Home > Press > A glass fiber that brings light to a standstill: By coupling photons to atoms, light in a glass fiber can be slowed down to the speed of an express train; for a short while it can even be brought to a complete stop
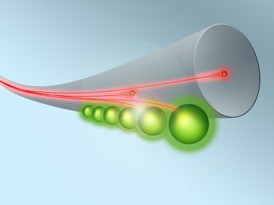 |
| Atoms coupled to a glass fiber: A system that can slow down light dramatically.
CREDIT: TU Wien |
Abstract:
Light is an extremely useful tool for quantum communication, but it has one major disadvantage: it usually travels at the speed of light and cannot be kept in place. A team of scientists at the Vienna University of Technology has now demonstrated that this problem can be solved - not only in strange, unusual quantum systems, but in the glass fiber networks we are already using today.
A glass fiber that brings light to a standstill: By coupling photons to atoms, light in a glass fiber can be slowed down to the speed of an express train; for a short while it can even be brought to a complete stop
Vienna, Austria | Posted on April 9th, 2015By coupling atoms to glass fibers light was slowed down to a speed of 180 km/h. The team even managed to bring the light to a complete stop and to retrieve it again later. This technology is an important prerequisite for a future glassfiber-based quantum-internet, in which quantum information can be teleported over great distances.
Light Pulses, Slower than an Express Train
In a vacuum, the speed of light is always the same - approximately 300 million meters per second. When light is sent through a medium such as glass or water, it is slowed down a little bit due to its interaction with the material. "In our system, this effect is extreme, because we are creating an exceedingly strong interaction between light and matter", says Professor Arno Rauschenbeutel (TU Wien / Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology). "The speed of light in our glass fiber is only 180 kilometers per hour. Any express train can top that."
Quantum Communication in Existing Fiber Networks
"There are different ways of quantum mechanically transferring information", says Clément Sayrin. "Glass fiber technology is a particularly attractive option - after all, a worldwide glass fiber net already exists, and we are already using it to transmit data."
At the TU Wien, cesium atoms are coupled to an ultrathin glass fiber. When the atom absorbs laser light it can pass from a state of low energy to a state of higher energy - provided that the energy of the absorbed photon matches the energy difference between the two states. This light, however, cannot be retrieved in a controlled way.
That is why the Viennese team used an additional control-laser in their experiment, which couples the high-energy state to a third atomic state. "The interplay between these three quantum states prevents the photon from just being absorbed and randomly emitted. Instead, the photon's quantum information is transferred to an ensemble of atoms in a controlled way, and it can be stored there for some time." The photon is turned into a collective excitation of atoms.
After two microseconds, a period of time in which the light would normally have travelled about half a kilometre, the control laser was used to prompt the atoms to emit the light back into the glass fiber. The properties of the photon stay exactly the same - an important prerequisite for quantum communication.
Being able to store photons is an important technological step towards quantum communication over great distances. "Quantum physics allows us to create a connection between sender and receiver, which makes eavesdropping impossible", says Arno Rauschenbeutel. "The fundamental laws of quantum physics make sure that no one can tap the connection without being noticed."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Florian Aigner
43-158-801-41027
Further information:
Dr. Christoph Clausen
Institute for Atomic and Subatomic Physics
Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology
TU Wien
Stadionallee 2, 1020 Wien
+43-1-58801-141713
Prof. Arno Rauschenbeutel
Institute for Atomic and Subatomic Physics
Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology
TU Wien
Stadionallee 2, 1020 Wien
T: +43-1-58801-141761
Copyright © Vienna University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








