Home > Press > Nanotechnology: Better measurements of single molecule circuits
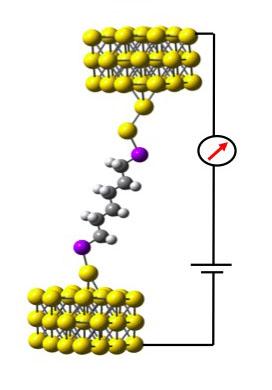 |
| A single molecule of hexane (six carbon atoms) with sulfur atoms at each end, between two gold electrodes. A new technique invented at UC Davis allows better measurements of the properties of such circuits and could boost research in nanotechnology. CREDIT: Josh Hihath/UC Davis |
Abstract:
It's nearly 50 years since Gordon Moore predicted that the density of transistors on an integrated circuit would double every two years. "Moore's Law" has turned out to be a self-fulfilling prophecy that technologists pushed to meet, but to continue into the future, engineers will have to make radical changes to the structure or composition of circuits. One potential way to achieve this is to develop devices based on single-molecule connections.
Nanotechnology: Better measurements of single molecule circuits
Davis, CA | Posted on February 18th, 2015New work by Josh Hihath's group at the UC Davis Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, published Feb. 16 in the journal Nature Materials, could help technologists make that jump. Hihath's laboratory has developed a method to measure the conformation of single molecule "wiring," resolving a clash between theoretical predictions and experiments.
"We're trying to make transistors and diodes out of single molecules, and unfortunately you can't currently control exactly how the molecule contacts the electrode or what the exact configuration is," Hihath said. "This new technique gives us a better measurement of the configuration, which will provide important information for theoretical modeling."
Until now, there has been a wide gap between the predicted electrical behavior of single molecules and experimental measurements, with results being off by as much as ten-fold, Hihath said.
Hihath's experiment uses a layer of alkanes (short chains of carbon atoms, such as hexane, octane or decane) with either sulfur or nitrogen atoms on each end that allow them to bind to a gold substrate that acts as one electrode. The researchers then bring the gold tip of a Scanning Tunneling Microscope towards the surface to form a connection with the molecules. As the tip is then pulled away, the connection will eventually consist of a single-molecule junction that contains six to ten carbon atoms (depending on the molecule studied at the time).
By vibrating the tip of the STM while measuring electrical current across the junction, Hihath and colleagues were able to extract information about the configuration of the molecules.
"This technique gives us information about both the electrical and mechanical properties of the system and tells us what the most probable configuration is, something that was not possible before," Hihath said.
The researchers hope the technique can be used to make better predictions of how molecule-scale circuits behave and design better experiments.
###
Coauthors on the paper are graduate students Habid Rascón-Ramos and Yuanhui Li and postdoctoral researcher Juan Manuel Artés, all at UC Davis. The work was supported by the National Science Foundation and the RISE program of the UC Davis Office of Research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andy Fell
530-752-4533
Copyright © University of California - Davis
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








