Home > Press > X-ray pulses uncover free nanoparticles for the first time in 3-D 'Super microscope' reveals unexpected variety of shapes
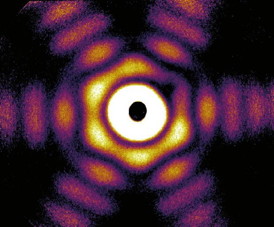 |
| This is a wide-angle X-ray diffraction image of a truncated twinned tetrahedra nanoparticle. CREDIT: Hannes Hartmann/University of Rostock: |
Abstract:
For the first time, a German-American research team has determined the three-dimensional shape of free-flying silver nanoparticles, using DESY's X-ray laser FLASH. The tiny particles, hundreds of times smaller than the width of a human hair, were found to exhibit an unexpected variety of shapes, as the physicists from the Technical University (TU) Berlin, the University of Rostock, the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in the United States and from DESY report in the scientific journal Nature Communications. Besides this surprise, the results open up new scientific routes, such as direct observation of rapid changes in nanoparticles.
X-ray pulses uncover free nanoparticles for the first time in 3-D 'Super microscope' reveals unexpected variety of shapes
Hamburg, Germany | Posted on February 4th, 2015Nanoparticles are becoming increasingly pervasive in our everyday lives. These tiny particles, invisible to the naked eye, have widespread applications, ranging from sunscreen and paints to colour filters and electronic components. They are even promising for medical purposes including cancer treatment. "The functionality of nanoparticles is linked to their geometric form, which is often very difficult to determine experimentally," explains Dr. Ingo Barke from the University of Rostock. "This is particularly challenging when they are present as free particles, that is, in the absence of contact with a surface or a liquid."
The nanoparticle shape can be revealed from the characteristic way how it scatters X-ray light. Therefore, X-ray sources like DESY's FLASH enable a sort of super microscope into the nano-world. So far, the spatial structure of nanoparticles has been reconstructed from multiple two-dimensional images, which were taken from different angles. This procedure is uncritical for particles on solid substrates, as the images can be taken from many different angles to uniquely reconstruct their three-dimensional shape.
"Bringing nanoparticles into contact with a surface or a liquid can significantly alter the particles, such that you can no longer see their actual form," says Dr. Daniela Rupp from the TU Berlin. A free particle, however, can only be measured one time in flight before it either escapes or is destroyed by the intense X-ray light. Therefore, the scientists looked for a way to record the entire structural information of a nanoparticle with a single X-ray laser pulse.
To achieve this goal, the scientists led by Prof. Thomas Möller from the TU Berlin and Prof. Karl-Heinz Meiwes-Broer and Prof. Thomas Fennel from the University of Rostock employed a trick. Instead of taking usual small-angle scattering images, the physicists recorded the scattered X-rays in a wide angular range. "This approach virtually captures the structure from many different angles simultaneously from a single laser shot," explains Fennel.
The researchers tested this method on free silver nanoparticles with diameters of 50 to 250 nanometres (0.00005 to 0.00025 millimetres). The experiment did not only verify the feasibility of the tricky method, but also uncovered the surprising result that large nanoparticles exhibit a much greater variety of shapes than expected.
The shape of free nanoparticles is a result of different physical principles, particularly the particles' effort to minimize their energy. Consequently, large particles composed of thousands or millions of atoms often yield predictable shapes, because the atoms can only be arranged in a particular way to obtain an energetically favourable state.
In their experiment, however, the researchers observed numerous highly symmetrical three-dimensional shapes, including several types known as Platonic and Archimedean bodies. Examples include the truncated octahedron (a body consisting of eight regular hexagons and six squares) and the icosahedron (a body made up of twenty equilateral triangles). The latter is actually only favourable for extremely small particles consisting of few atoms, and its occurrence with free particles of this size was previously unknown. "The results show that metallic nanoparticles retain a type of memory of their structure, from the early stages of growth to a yet unexplored size range," emphasizes Barke.
Due to the large variety of shapes, it was especially important to use a fast computational method so that the researchers were capable of mapping the shape of each individual particle. The scientists used a two-step process: the rough shape was determined first and then refined using more complex simulations on a super computer. This approach turned out to be so efficient that it could not only determine various shapes reliably, but could also differentiate between varying orientations of the same shape.
This new method for determining the three-dimensional shape and orientation of nanoparticles with a single X-ray laser shot opens up a wide spectrum of new research directions. In future projects, particles could be directly "filmed" in three dimensions during growth or during phase changes. "The ability to directly film the reaction of a nanoparticle to an intense flash of X-ray light has been a dream for many physicists - this dream could now come true, even in 3D!," emphasises Rupp.
####
About Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY
Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY is the leading German accelerator centre and one of the leading in the world. DESY is a member of the Helmholtz Association and receives its funding from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) (90 per cent) and the German federal states of Hamburg and Brandenburg (10 per cent). At its locations in Hamburg and Zeuthen near Berlin, DESY develops, builds and operates large particle accelerators, and uses them to investigate the structure of matter. DESY's combination of photon science and particle physics is unique in Europe.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Thomas Zoufal
49-408-998-1666
Copyright © Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








