Home > Press > Nano-beaker offers insight into the condensation of atoms
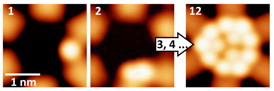 |
| Depicted in scanning tunneling microscopy are three different quantum wells that contain one, two and three xenon atoms. CREDIT: University of Basel |
Abstract:
An international team of physicists has succeeded in mapping the condensation of individual atoms, or rather their transition from a gaseous state to another state, using a new method. Led by the Swiss Nanoscience Institute and the Department of Physics at the University of Basel, the team was able to monitor for the first time how xenon atoms condensate in microscopic measuring beakers, or quantum wells, thereby enabling key conclusions to be drawn as to the nature of atomic bonding. The researchers published their results in the journal Nature Communications.
Nano-beaker offers insight into the condensation of atoms
Basel, Switzerland | Posted on January 21st, 2015The team headed by Professor Thomas Jung, which consists of researchers from the Swiss Nanoscience Institute, Department of Physics at the University of Basel and the Paul Scherrer Institute, developed a method enabling the condensation of individual atoms to be mapped on a step by step basis for the first time. The researchers allowed atoms of the noble gas xenon to condensate in quantum wells and monitored the resulting accumulations using a scanning tunneling microscope.
Quantum wells as beakers
The autonomous organization of specifically 'programmed' molecules facilitates the creation of a porous network on a substrate surface - these are the quantum wells used as measuring beakers with a specifically defined size, shape and atomic wall and floor structure. The atoms' freedom of movement is restricted in the quantum wells, allowing the arrangement of the atoms to be closely monitored and mapped depending on the composition.
With this data, the researchers were able to show that the xenon atoms always arrange themselves according to a certain principle. For example, some units consisting of four atoms are only formed when there are at least seven atoms in the quantum well. And if there are twelve atoms in the quantum well, this results in the creation of three highly stable four-atom units.
Conclusions about the nature of bonding
The images and structures of nano-condensates recorded for the first time allow key conclusions to be drawn as to the nature of the physical bonds formed by the xenon atoms. "But this system is not restricted exclusively to noble gases," says Sylwia Nowakowska, lead author of the publication. "We can also use it to research other atoms and the way that they bond." As the newly developed method accurately maps atomic bonding and determines the stability of the various states, it can also be used to verify theoretical calculations about bonds.
The results of the study are based on a collaboration between researchers from Switzerland, Brazil, Sweden, Germany and the Netherlands, and were published in the current issue of the scientific journal Nature Communications.
###
Original source
Sylwia Nowakowska, Aneliia Wäckerlin, Shigeki Kawai, Toni Ivas, Jan Nowakowski, Shadi Fatayer, Christian Wäckerlin, Thomas Nijs, Ernst Meyer, Jonas Björk, Meike Stöhr, Lutz H. Gade & Thomas A. Jung
Interplay of weak interactions in the atom-by-atom condensation of xenon within quantum boxes
Nature Communications 2015, DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7071
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Olivia Poisson
Copyright © University of Basel
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








