Home > Press > Atoms can be in 2 places at the same time: Researchers of the University of Bonn have shown that cesium atoms do not follow well-defined paths
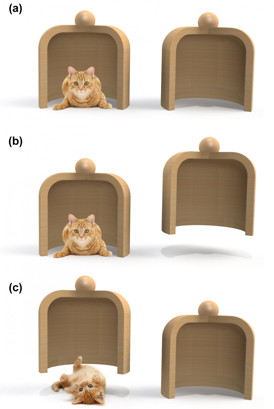 |
| The Bonn team has developed a measurement scheme that indirectly measures the position of an atom. In essence, one looks where the cesium atom is not. The image clarifies this procedure. Let us assume that two containers are in front of us and a cat is hidden under one of them (a). However, we do not know under which one. We tentatively lift the right jar (b) and we find it empty. We, thus, conclude that the cat must be in the left jar and yet we have not disturbed it. Had we have lifted the left jar instead, we would have disturbed the cat (c), and the measurement must be discarded. In the macro-realist's world, this measurement scheme would have absolutely no influence on the cat's state, which remains undisturbed all the time. In the quantum world, however, a negative measurement that reveals the cat's position, like in (b), is already sufficient to destroy the quantum superposition and to influence the result of the experiment. The Bonn physicists have exactly observed this effect.
CREDIT: Andrea Alberti / www.warrenphotographic.co.uk |
Abstract:
Can a penalty kick simultaneously score a goal and miss? For very small objects, at least, this is possible: according to the predictions of quantum mechanics, microscopic objects can take different paths at the same time. The world of macroscopic objects follows other rules: the football always moves in a definite direction. But is this always correct? Physicists of the University of Bonn have constructed an experiment designed to possibly falsify this thesis. Their first experiment shows that Caesium atoms can indeed take two paths at the same time.
Atoms can be in 2 places at the same time: Researchers of the University of Bonn have shown that cesium atoms do not follow well-defined paths
Bonn, Germany | Posted on January 20th, 2015Almost 100 years ago physicists Werner Heisenberg, Max Born und Erwin Schrödinger created a new field of physics: quantum mechanics. Objects of the quantum world - according to quantum theory - no longer move along a single well-defined path. Rather, they can simultaneously take different paths and end up at different places at once. Physicists speak of quantum superposition of different paths.
At the level of atoms, it looks as if objects indeed obey quantum mechanical laws. Over the years, many experiments have confirmed quantum mechanical predictions. In our macroscopic daily experience, however, we witness a football flying along exactly one path; it never strikes the goal and misses at the same time. Why is that so?
"There are two different interpretations," says Dr. Andrea Alberti of the Institute of Applied Physics of the University of Bonn. "Quantum mechanics allows superposition states of large, macroscopic objects. But these states are very fragile, even following the football with our eyes is enough to destroy the superposition and makes it follow a definite trajectory."
Do "large" objects play by different rules?
But it could also be that footballs obey completely different rules than those applying for single atoms. "Let us talk about the macro-realistic view of the world," Alberti explains. "According to this interpretation, the ball always moves on a specific trajectory, independent of our observation, and in contrast to the atom."
But which of the two interpretations is correct? Do "large" objects move differently from small ones? In collaboration with Dr. Clive Emary of the University of Hull in the U.K., the Bonn team has come up with an experimental scheme that may help to answer this question. "The challenge was to develop a measurement scheme of the atoms' positions which allows one to falsify macro-realistic theories," adds Alberti.
The physicists describe their research in the journal Physical Review X: With two optical tweezers they grabbed a single Caesium atom and pulled it in two opposing directions. In the macro-realist's world the atom would then be at only one of the two final locations. Quantum-mechanically, the atom would instead occupy a superposition of the two positions.
"We have now used indirect measurements to determine the final position of the atom in the most gentle way possible," says the PhD student Carsten Robens. Even such an indirect measurement (see figure) significantly modified the result of the experiments. This observation excludes - falsifies, as Karl Popper would say more precisely - the possibility that Caesium atoms follow a macro-realistic theory. Instead, the experimental findings of the Bonn team fit well with an interpretation based on superposition states that get destroyed when the indirect measurement occurs. All that we can do is to accept that the atom has indeed taken different paths at the same time.
"This is not yet a proof that quantum mechanics hold for large objects," cautions Alberti. "The next step is to separate the Caesium atom's two positions by several millimetres. Should we still find the superposition in our experiment, the macro-realistic theory would suffer another setback."
###
Publication: Carsten Robens, Wolfgang Alt, Dieter Meschede, Clive Emary und Andrea Alberti: Ideal negative measurements in quantum walks disprove theories based on classical trajectories; Physical Review X, 20.1.2015 (DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevX.5.011003)
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Andrea Alberti
0049-228-733-483
Copyright © University of Bonn
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








