Home > Press > Two sensors in one: Nanoparticles that enable both MRI and fluorescent imaging could monitor cancer, other diseases
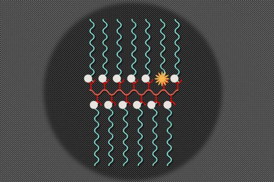 |
| Illustration: Christine Daniloff/MIT |
Abstract:
MIT chemists have developed new nanoparticles that can simultaneously perform magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and fluorescent imaging in living animals. Such particles could help scientists to track specific molecules produced in the body, monitor a tumor's environment, or determine whether drugs have successfully reached their targets.
Two sensors in one: Nanoparticles that enable both MRI and fluorescent imaging could monitor cancer, other diseases
Cambridge, MA | Posted on November 18th, 2014
In a paper appearing in the Nov. 18 issue of Nature Communications, the researchers demonstrate the use of the particles, which carry distinct sensors for fluorescence and MRI, to track vitamin C in mice. Wherever there is a high concentration of vitamin C, the particles show a strong fluorescent signal but little MRI contrast. If there is not much vitamin C, a stronger MRI signal is visible but fluorescence is very weak.
Future versions of the particles could be designed to detect reactive oxygen species that often correlate with disease, says Jeremiah Johnson, an assistant professor of chemistry at MIT and senior author of the study. They could also be tailored to detect more than one molecule at a time.
"You may be able to learn more about how diseases progress if you have imaging probes that can sense specific biomolecules," Johnson says.
Dual action
Johnson and his colleagues designed the particles so they can be assembled from building blocks made of polymer chains carrying either an organic MRI contrast agent called a nitroxide or a fluorescent molecule called Cy5.5.
When mixed together in a desired ratio, these building blocks join to form a specific nanosized structure the authors call a branched bottlebrush polymer. For this study, they created particles in which 99 percent of the chains carry nitroxides, and 1 percent carry Cy5.5.
Nitroxides are reactive molecules that contain a nitrogen atom bound to an oxygen atom with an unpaired electron. Nitroxides suppress Cy5.5's fluorescence, but when the nitroxides encounter a molecule such as vitamin C from which they can grab electrons, they become inactive and Cy5.5 fluoresces.
Nitroxides typically have a very short half-life in living systems, but University of Nebraska chemistry professor Andrzej Rajca, who is also an author of the new Nature Communications paper, recently discovered that their half-life can be extended by attaching two bulky structures to them. Furthermore, the authors of the Nature Communications paper show that incorporation of Rajca's nitroxide in Johnson's branched bottlebrush polymer architectures leads to even greater improvements in the nitroxide lifetime. With these modifications, nitroxides can circulate for several hours in a mouse's bloodstream — long enough to obtain useful MRI images.
The researchers found that their imaging particles accumulated in the liver, as nanoparticles usually do. The mouse liver produces vitamin C, so once the particles reached the liver, they grabbed electrons from vitamin C, turning off the MRI signal and boosting fluorescence. They also found no MRI signal but a small amount of fluorescence in the brain, which is a destination for much of the vitamin C produced in the liver. In contrast, in the blood and kidneys, where the concentration of vitamin C is low, the MRI contrast was maximal.
Mixing and matching
The researchers are now working to enhance the signal differences that they get when the sensor encounters a target molecule such as vitamin C. They have also created nanoparticles carrying the fluorescent agent plus up to three different drugs. This allows them to track whether the nanoparticles are delivered to their targeted locations.
"That's the advantage of our platform — we can mix and match and add almost anything we want," Johnson says.
These particles could also be used to evaluate the level of oxygen radicals in a patient's tumor, which can reveal valuable information about how aggressive the tumor is.
"We think we may be able to reveal information about the tumor environment with these kinds of probes, if we can get them there," Johnson says. "Someday you might be able to inject this in a patient and obtain real-time biochemical information about disease sites and also healthy tissues, which is not always straightforward."
Steven Bottle, a professor of nanotechnology and molecular science at Queensland University of Technology, says the most impressive element of the study is the combination of two powerful imaging techniques into one nanomaterial.
"I believe this should deliver a very powerful, metabolically linked, multi-combination imaging modality which should provide a highly useful diagnostic tool with real potential to follow disease progression in vivo," says Bottle, who was not involved in the study.
The research was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Defense, the National Science Foundation, and the Koch Institute for Integrative Cancer Research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah McDonnell
617-253-8923
Copyright © Massachusetts Institute of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Cancer
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








