Home > Press > Researchers discern the shapes of high-order Brownian motions
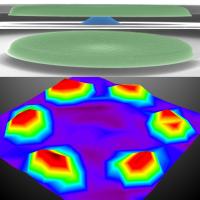 |
| This image spatially maps and visualizes the shapes of multimode Brownian motions. The to of the image is a false-colored scanning electron micrographs of a silicon carbide (SiC) microdisk supported by a central pedestal made of 500nm-thick silicon oxide. The bottom image is a scanned map of vibrations of the microdisk due to a high-order mode Brownian motion.
Credit: Philip Feng |
Abstract:
For the first time, scientists have vividly mapped the shapes and textures of high-order modes of Brownian motions--in this case, the collective macroscopic movement of molecules in microdisk resonators--researchers at Case Western Reserve University report.
Researchers discern the shapes of high-order Brownian motions
Cleveland, OH | Posted on November 17th, 2014To do this, they used a record-setting scanning optical interferometry technique, described in a study published today in the journal Nature Communications.
The new technology holds promise for multimodal sensing and signal processing, and to develop optical coding for computing and other information-processing functions by exploiting the spatially resolved multimode Brownian resonances and their splitting pairs of modes.
"What we found agrees with the expected Brownian motions in high-order modes," said Philip Feng, assistant professor of electrical engineering and computer science at Case Western Reserve and senior author of the study. "But it has been pretty amazing and exhilarating to directly visualize these modes down to the fundamental limit of intrinsic Brownian motions."
In his lab at Case School of Engineering, Feng worked closely with research associate Max Zenghui Wang and PhD student Jaesung Lee on the study.
Interferometry uses the interference of light waves reflected off a surface to measure distances, a technique invented by Case School of Applied Science physicist Albert A. Michelson (who won the Nobel prize in science in 1907). Michelson and Western Reserve University chemist Edward Morley used the instrument to famously disprove that light traveled through "luminous ether" in 1887, setting the groundwork for Albert Einstein's theory of relativity.
The technology has evolved since then. The keys to Feng's new interferometry technique are focusing a tighter-than-standard laser spot on the surface of novel silicon carbide microdisks.
The microdisks, which sit atop pedestals of silicon oxide like cymbals on stands, are extremely sensitive to the smallest fluctuations arising from Brownian motions, even at thermodynamic equilibrium. Hence, they exhibit very small oscillations without external driving forces. These oscillations include fundamental and higher modes, called thermomechanical resonances.
Some of the light from the laser reflects back to a sensor after striking the top surface of the silicon dioxide film. And some of the light is refracted through the film and reflected back on a different path, causing interference in the light waves.
The narrow laser spot scans the disk surface and measures movement, or displacement, of the disk with a sensitivity of about 7 femtometers per square-root of a hertz at room temperature, which researchers believe is a record for interferometric systems. To put that in perspective, the width of a hair is about 40 microns, and a femtometer is 100 million times smaller than a micron.
Although higher frequency modes have small motion amplitudes, the technology enabled the group to spatially map and clearly visualize the first through ninth Brownian modes in the high frequency band, ranging from 5.78 to 26.41 megahertz.
In addition to detecting the shapes and textures of Brownian motions, multimode mapping identified subtle structural imperfections and defects, which are ubiquitous but otherwise invisible, or can't be quantified most of the time. This capability may be useful for probing the dynamics and propagation of defects and defect arrays in nanodevices, as well as for future engineering of controllable defects to manipulate information in silicon carbide nanostructures.
The high sensitivity and spatial resolution also enabled them to identify mode splitting, crossing and degeneracy, spatial asymmetry and other effects that may be used to encode information with increasing complexity. The researchers are continuing to explore the capabilities of the technology.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kevin Mayhood
216-534-7183
Copyright © Case Western Reserve University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








