Home > Press > Nano Ruffles in Brain Matter: Freiburg researchers decipher the role of nanostructures around brain cells in central nervous system function
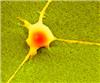 |
| Scanning electron micrograph showing a neuron on a nanorough surface making intimate contact with the surface. Surfaces has been given a false color for visualization. Source: Nils Blumenthal and Prasad Shastri |
Abstract:
An accumulation of a protein called amyloid-beta into large insoluble deposits called plaques is known to cause Alzheimer's disease. One aspect of this illness that has not received much attention is which role the structure of the brain environment plays. How do macromolecules and macromolecular assemblies, such as polysaccharides, influence cell interaction in the brain? In a paper published in the journal "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences", Prof. Prasad Shastri and graduate student Nils Blumenthal, in collaboration with Prof. Bernd Heimrich and Prof. Ola Hermanson, have discovered that macromolecules or support cells like astrocytes provide well-defined physical cues in the form of random roughness or ruffles that have a crucial role in promoting and maintaining healthy interactions between cells in the hippocampus. This brain area is regarded as the brain's GPS system: It processes and stores spatial information. In Alzheimer's disease, this area degenerates. Shastri says, "It has been long thought that only biological signals have a role in health and function of brain cells, but here we show that the structure of the molecules that surround these cells may be equally important."
Nano Ruffles in Brain Matter: Freiburg researchers decipher the role of nanostructures around brain cells in central nervous system function
Freiburg, Germany | Posted on October 31st, 2014The researchers found that there is a restricted regime of roughness at the nanoscale that is beneficial to neurons. If the magnitude of roughness exceeds or is below this regime, neurons experience detrimental changes to their function. By analyzing human brain tissue from patients who suffered from Alzheimer's disease, Shastri's team has found a crucial link between regions in the brain that have amyloid-beta plaque accumulation - which are responsible for neuron death - and unfavorable changes to the nanotopography in the tissue surrounding these neurons, that is the features of its surface..
Shastri and his co-workers have found that astrocytes provide a nanoscale physical environment that neurons need to function well. "Our discovery shows for the first time that stretch-activated ion channels may have a role in central nervous system function and disease. Hence, our findings offer new pharmacological targets", says Blumenthal. Using synthetic substrates of precise roughness, they found out that stretch-sensitive molecules, including the so-called Piezo-1 ion channel in murine brain cells, direct the interaction between nanotopography, astrocytes and neurons. Former research has shown that the expression of MIB-1, a human analog of Piezo-1, is altered in human Alzheimer's patients.
Prof. Prasad Shastri conducts his research at the Institute for Macromolecular Chemistry and the Excellence Cluster BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies of the University of Freiburg. Graduate student Nils Blumenthal is funded by BIOSS. Prof. Bernd Heimrich is at the Institute of Anatomy and Cell Biology of the University of Freiburg and Prof. Ola Hermanson is from the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm/Sweden.
####
About Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg
The University of Freiburg was founded in 1457 as a classical comprehensive university, making it one of the oldest higher education institutions in Germany. Successful in the Excellence Initiative, the university also boasts an illustrious history with numerous Nobel Prize recipients. Brilliant scholars and creative thinking distinguish it today as a modern top-notch university well equipped for the challenges of the 21st century.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Katrin Albaum
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Full bibliographic information
Full bibliographic information
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








