Home > Press > Beyond LEDs: Brighter, new energy-saving flat panel lights based on carbon nanotubes - Planar light source using a phosphor screen with highly crystalline single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) as field emitters demonstrates its potential for energy-efficient lighting device
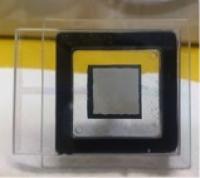 |
| This image shows a planar light source device from the front.
Credit: N.Shimoi/Tohoku University |
Abstract:
Even as the 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics has enshrined light emitting diodes (LEDs) as the single most significant and disruptive energy-efficient lighting solution of today, scientists around the world continue unabated to search for the even-better-bulbs of tomorrow.
Beyond LEDs: Brighter, new energy-saving flat panel lights based on carbon nanotubes - Planar light source using a phosphor screen with highly crystalline single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) as field emitters demonstrates its potential for energy-efficient lighting device
Washington, DC | Posted on October 14th, 2014Enter carbon electronics.
Electronics based on carbon, especially carbon nanotubes (CNTs), are emerging as successors to silicon for making semiconductor materials. And they may enable a new generation of brighter, low-power, low-cost lighting devices that could challenge the dominance of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) in the future and help meet society's ever-escalating demand for greener bulbs.
Scientists from Tohoku University in Japan have developed a new type of energy-efficient flat light source based on carbon nanotubes with very low power consumption of around 0.1 Watt for every hour's operation--about a hundred times lower than that of an LED.
In the journal Review of Scientific Instruments, from AIP publishing, the researchers detail the fabrication and optimization of the device, which is based on a phosphor screen and single-walled carbon nanotubes as electrodes in a diode structure. You can think of it as a field of tungsten filaments shrunk to microscopic proportions.
They assembled the device from a mixture liquid containing highly crystalline single-walled carbon nanotubes dispersed in an organic solvent mixed with a soap-like chemical known as a surfactant. Then, they "painted" the mixture onto the positive electrode or cathode, and scratched the surface with sandpaper to form a light panel capable of producing a large, stable and homogenous emission current with low energy consumption.
"Our simple 'diode' panel could obtain high brightness efficiency of 60 Lumen per Watt, which holds excellent potential for a lighting device with low power consumption," said Norihiro Shimoi, the lead researcher and an associate professor of environmental studies at the Tohoku University.
Brightness efficiency tells people how much light is being produced by a lighting source when consuming a unit amount of electric power, which is an important index to compare the energy-efficiency of different lighting devices, Shimoi said. For instance, LEDs can produce 100s Lumen per Watt and OLEDs (organic LEDs) around 40.
Although the device has a diode-like structure, its light-emitting system is not based on a diode system, which are made from layers of semiconductors, materials that act like a cross between a conductor and an insulator, the electrical properties of which can be controlled with the addition of impurities called dopants.
The new devices have luminescence systems that function more like cathode ray tubes, with carbon nanotubes acting as cathodes, and a phosphor screen in a vacuum cavity acting as the anode. Under a strong electric field, the cathode emits tight, high-speed beams of electrons through its sharp nanotube tips -- a phenomenon called field emission. The electrons then fly through the vacuum in the cavity, and hit the phosphor screen into glowing.
"We have found that a cathode with highly crystalline single-walled carbon nanotubes and an anode with the improved phosphor screen in our diode structure obtained no flicker field emission current and good brightness homogeneity," Shimoi said.
Field emission electron sources catch scientists' attention due to its ability to provide intense electron beams that are about a thousand times denser than conventional thermionic cathode (like filaments in an incandescent light bulb). That means field emission sources require much less power to operate and produce a much more directional and easily controllable stream of electrons.
In recent years, carbon nanotubes have emerged as a promising material of electron field emitters, owing to their nano-scale needle shape and extraordinary properties of chemical stability, thermal conductivity and mechanical strength.
Highly crystalline single-walled carbon nanotubes (HCSWCNT) have nearly zero defects in the carbon network on the surface, Shimoi explained. "The resistance of cathode electrode with highly crystalline single-walled carbon nanotube is very low. Thus, the new flat-panel device has smaller energy loss compared with other current lighting devices, which can be used to make energy-efficient cathodes that with low power consumption."
"Many researchers have attempted to construct light sources with carbon nanotubes as field emitter," Shimoi said. "But nobody has developed an equivalent and simpler lighting device."
Considering the major step for device manufacture--the wet coating process is a low-cost but stable process to fabricate large-area and uniformly thin films, the flat-plane emission device has the potential to provide a new approach to lighting in people's life style and reduce carbon dioxide emissions on the earth, Shimoi said.
####
About American Institute of Physics
The journal Review of Scientific Instruments, which is produced by AIP Publishing, presents innovation in instrumentation and methods across disciplines. See: rsi.aip.org/
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jason Socrates Bardi
240-535-4954
Copyright © American Institute of Physics
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








