Home > Press > UO-Berkeley Lab unveil new nano-sized synthetic scaffolding technique: Oil-and-water approach from Richmond's UO lab to spark new line of versatile peptoid nanosheets
 |
Abstract:
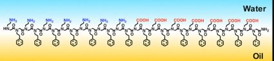
Scientists, including University of Oregon chemist Geraldine Richmond, have tapped oil and water to create scaffolds of self-assembling, synthetic proteins called peptoid nanosheets that mimic complex biological mechanisms and processes.
UO-Berkeley Lab unveil new nano-sized synthetic scaffolding technique: Oil-and-water approach from Richmond's UO lab to spark new line of versatile peptoid nanosheets
Eugene, OR | Posted on September 2nd, 2014The accomplishment -- detailed this week in a paper placed online ahead of print by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences -- is expected to fuel an alternative design of the two-dimensional peptoid nanosheets that can be used in a broad range of applications. Among them could be improved chemical sensors and separators, and safer, more effective drug-delivery vehicles.
Study co-author Ronald Zuckermann of the Molecular Foundry at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) first developed these ultra-thin nanosheets in 2010 using an air-and-water combination.
"We often think of oil on water as something that is environmentally bad when, in fact, my group over the past 20 years has been studying the unique properties of the junction between water and oil as an interesting place for molecules to assemble in unique ways -- including for soaps and oil dispersants," said Richmond, who holds a UO presidential chair. "This study shows it is also a unique platform for making nanosheets."
Lead authors on the project were Ellen J. Robertson, a doctoral student in Richmond's lab at the time of the research, and Gloria K. Oliver, a postdoctoral researcher at LBNL. Robertson is now a postdoctoral researcher at LBNL.
Work in Richmond's lab helped to identify the mechanism behind the formation of the nanosheets at an oil-water interface.
"Supramolecular assembly at an oil-water interface is an effective way to produce 2D nanomaterials from peptoids because that interface helps pre-organize the peptoid chains to facilitate their self-interaction," said Zuckermann, a senior scientist at LBNL's Molecular Foundry in a news release. "This increased understanding of the peptoid assembly mechanism should enable us to scale-up to produce large quantities, or scale- down, using microfluidics, to screen many different nanosheets for novel functions."
Zuckermann and Richmond are the corresponding authors on the paper. Additional co-authors are Menglu Qian and Caroline Proulx, both of LBNL.
Like natural proteins, synthetic proteins fold and conform into structures that allow them to do specific functions. In his earlier work, Zuckermann's team at LBNL's Molecular Foundry discovered a technique to synthesize peptoids into sheets that were just a few nanometers thick but up to 100 micrometers in length. These were among the largest and thinnest free-floating organic crystals ever made, with an area-to-thickness equivalent of a plastic sheet covering a football field.
"Peptoid nanosheet properties can be tailored with great precision," Zuckermann says, "and since peptoids are less vulnerable to chemical or metabolic breakdown than proteins, they are a highly promising platform for self-assembling bio-inspired nanomaterials."
To create the new version of the nanosheets, the research team used vibrational sum frequency spectroscopy to probe the molecular interactions between the peptoids as they assemble at the oil-water interface. The work showed that peptoid polymers adsorbed to the interface are highly ordered in a way that is influenced by interactions between neighboring molecules.
The substitution of oil in place of air creates a raft of new opportunities for the engineering and production of peptoid nanosheets, the researchers said. The oil phase, for example, could contain chemical reagents, serve to minimize evaporation of the aqueous phase or enable microfluidic production.
###
The U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Basic Energy Sciences (grant DE-FG02-96ER45557) supported the research done in Richmond's UO lab. Work at the Molecular Foundry at LBNL was supported by the DOE (under contract DE-AC02-05CH11231) and the Defense Threat Reduction Agency (grant IACRO-B1144571).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jim Barlow
541-346-3481
Sources: Geraldine Richmond is traveling but can be reached through the media contact above;
Ronald Zuckermann
Molecular Foundry
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
510-486-7091
Copyright © University of Oregon
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Microfluidics/Nanofluidics
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








