Home > Press > A breakthrough in imaging gold nanoparticles to atomic resolution by electron microscopy
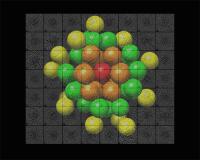 |
| This is a visualization of the atomic structure of the Au68 gold nanoparticle determined by electron microscopy. The colored spheres denote gold atoms in different crystal shells around the central axis (red). The background shows a collection of real-life electron microscopy data from which the single structure shown was reconstructed.
Credit: Copyright Maia Azubel, Stanford University. |
Abstract:
Nanometre-scale gold particles are intensively investigated for application as catalysts, sensors, drug delivery devices, biological contrast agents and components in photonics and molecular electronics. Gaining knowledge of their atomic-scale structures, fundamental for understanding physical and chemical properties, has been challenging. Now, researchers at Stanford University, USA, have demonstrated that high-resolution electron microscopy can be used to reveal a three-dimensional structure in which all gold atoms are observed. The results are in close agreement with a structure predicted at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland, on the basis of theoretical modelling and infrared spectroscopy (see Figure). The research was published in Science on 22 August 2014.
A breakthrough in imaging gold nanoparticles to atomic resolution by electron microscopy
Helsinki, Finland | Posted on August 22nd, 2014The revealed gold nanoparticle is 1.1 nm in diameter and contains 68 gold atoms organised in a crystalline fashion at the centre of the particle. The result was supported by small-angle X-ray scattering done in Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, USA, and by mass spectrometry done at Hokkaido University, Japan.
Electron microscopy is similar in principle to conventional light microscopy, with the exception that the wavelength of the electron beam used for imaging is close to the spacing of atoms in solid matter, about a tenth of a nanometre, in contrast with the wavelength of visible light, which is hundreds of nanometres. A crucial aspect of the new work is the irradiation of the nanoparticle with very few electrons to avoid perturbing the structure of the nanoparticle. The success of this approach opens the way to the determination of many more nanoparticle structures and to both fundamental understanding and practical applications.
The researchers involved in the work are Maia Azubel, Ai Leen Koh, David Bushnell and Roger D. Kornberg from Stanford University, Sami Malola, Jaakko Koivisto, Mika Pettersson and Hannu Häkkinen from the University of Jyväskylä, Greg L. Hura from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, and Tatsuya Tsukuda and Hironori Tsunoyama from Hokkaido University. The work at the University of Jyväskylä was supported by the Academy of Finland. The computational work in Hannu Häkkinen's group was done at the HLRS-GAUSS centre in Stuttgart as part of the PRACE project "Nano-gold at the bio-interface".
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Professor Roger D. Kornberg
Stanford University
Professor Hannu Häkkinen
University of Jyväskylä
Academy of Finland Communications
Communications Specialist Leena Vähäkylä
tel. +358 295 335 139
firstname.lastname(at)aka.fi
Copyright © Academy of Finland
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








