Home > Press > Nanocubes Get in a Twist : Competing forces coax nanocubes into helical structures
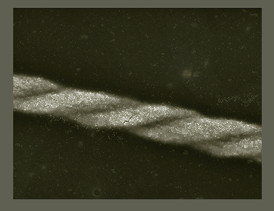 |
| SEM image of a well-defined double helix |
Abstract:
Nanocubes are anything but child's play. Weizmann Institute scientists have used them to create surprisingly yarn-like strands: They showed that given the right conditions, cube-shaped nanoparticles are able to align into winding helical structures. Their results, which reveal how nanomaterials can self-assemble into unexpectedly beautiful and complex structures, were recently published in Science.
Nanocubes Get in a Twist : Competing forces coax nanocubes into helical structures
Rehovot, Israel | Posted on August 11th, 2014Dr. Rafal Klajn and postdoctoral fellow Dr. Gurvinder Singh of the Institute's Organic Chemistry Department used nanocubes of an iron oxide material called magnetite. As the name implies, this material is naturally magnetic: It is found all over the place, including inside bacteria that use it to sense the Earth's magnetic field.
Magnetism is just one of the forces acting on the nanoparticles. Together with the research group of Prof. Petr Král of the University of Illinois, Chicago, Klajn and Singh developed theoretical models to understand how the various forces could push and pull the tiny bits of magnetite into different formations. "Different types of forces compel the nanoparticles to align in different ways," says Klajn. "These can compete with one another; so the idea is to find the balance of competing forces that can induce the self-assembly of the particles into novel materials." The models suggested that the shape of the nanoparticles is important - only cubes would provide a proper balance of forces required for pulling together into helical formations.
The researchers found that the two main competing forces are magnetism and the van der Waals force. Magnetism causes the magnetic particles to both attract and repel one another, prompting the cubic particles to align at their corners. Van der Waals forces, on the other hand, pull the sides of the cubes closer together, coaxing them to line up in a row. When these forces act together on the tiny cubes, the result is the step-like alignment that produces helical structures.
In their experiments, the scientists exposed relatively high concentrations of magnetite nanocubes placed in a solution to a magnetic field. The long, rope-like helical chains they obtained after the solution was evaporated were surprisingly uniform. They repeated the experiment with nanoparticles of other shapes but, as predicted, only cubes had just the right physical shape to align in a helix. Klajn and Singh also found that they could get chiral strands - all wound in the same direction - with very high particle concentrations in which a number of strands assembled closely together. Apparently the competing forces can "take into consideration" the most efficient way to pack the strands into the space.
Although the nanocube strands look nice enough to knit, Klajn says it is too soon to begin thinking of commercial applications. The immediate value of the work, he says, is that it has proven a fundamental principle of nanoscale self-assembly. "Although magnetite has been well-studied - also its nanoparticle form - for many decades, no one has observed these structures before," says Klajn. "Only once we understand how the various physical forces act on nanoparticles can we begin to apply the insights to such goals as the fabrication of previously unknown, self-assembled materials."
Dr. Rafal Klajn's research is supported by the Abramson Family Center for Young Scientists; the estate of Olga Klein Astrachan; and the European Research Council.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Yivsam Azgad
972-893-43852
Copyright © The Weizmann Institute of Science
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








