Home > Press > New analysis eliminates a potential speed bump in quantum computing: Global symmetry not required for fast quantum search
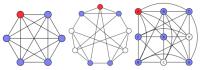 |
| In a complete graph (left) every node is connected to every other. For other well studied graphs, the Paley graph in the center and the Latin square graph on the right, that is not true. A quantum particle could hop directly to the target position, in red, only from connected nodes, marked in blue.
Credit: Tom Wong, UC San Diego |
Abstract:
A quantum particle can search for an item in an unsorted "database" by jumping from one item to another in superposition, and it does so faster than a classical computer ever could.
New analysis eliminates a potential speed bump in quantum computing: Global symmetry not required for fast quantum search
San Diego, CA | Posted on May 21st, 2014This assertion assumes, however, that the particle can directly hop from any item to any other. Any restriction on which items the particle can directly hop to could slow down the search.
"Intuition says that a symmetric database allows the particle to hop freely enough to retain the quantum speedup, but our research has shown this intuition to be false," says Tom Wong, a physicist at the University of California, San Diego.
In a paper accepted for publication by Physical Review Letters, the researchers used a technique familiar to physicists called "degenerate perturbation theory" in a novel way to prove that global symmetry is not required for a sped up search.
Information scientists represent the database to be searched as a graph. In globally symmetric graphs, the nodes can be swapped with each other such that the connections between them are preserved. "Strongly regular graphs" don't share this property, but this analysis shows they also support a fast search through local symmetries.
Their finding extends the use of this theory to the field of quantum information science and expands the kinds of data structures on which quantum computing outperforms classical computing.
###
Jonatan Janmark, KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, Sweden and UC San Diego's Department of Mathematics and David Meyer, professor of mathematics at UC San Diego co-authored the work.
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency partially supported this work as part of its Quantum Entanglement Science and Technology program. Additional funding came from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research as part of the Transformational Computing in Aerospace Science and Engineering Initiative, and the Achievement Awards for College Scientists Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Tom Wong
Copyright © University of California - San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








