Home > Press > Protein sharpens salmonella needle for attack
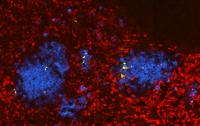 |
| This image depicts a section of a Salmonella infected spleen in yellow, red blood cells in red and neutrophils in blue.
Credit: Illustration: University of Basel, Biozentrum |
Abstract:
A tiny nanoscale syringe is Salmonella's weapon. Using this, the pathogen injects its molecular agents into the host cells and manipulates them to its own advantage. A team of scientists at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel demonstrate in their current publication in Cell Reports that a much investigated protein, which plays a role in Salmonella metabolism, is required to activate these needles and makes the replication and spread of Salmonella throughout the whole body possible.
Protein sharpens salmonella needle for attack
Basel, Switzerland | Posted on May 15th, 2014The summer months are the prime time for Salmonella infections. Such an infection is caused by the ingestion of contaminated food, for instance ice cream or raw eggs, and can cause severe diarrhea. Salmonella can even cause life-threatening illnesses such as typhoid fever.
For several years, Prof. Dirk Bumann, from the Biozentrum of the University of Basel, has been studying the infection mechanisms of Salmonella. Together with his team, he has discovered that the bacterial protein EIIAGlc is not only responsible for the uptake of nutrients, which was previously known, but also plays a central role in Salmonella colonizing the host organism.
New function discovered for well known protein
Salmonella possesses a sophisticated injection apparatus, the type III secretion system. With this molecular syringe, it injects toxins directly into the host cells. These toxins manipulate host cell processes to create optimal growth conditions for the bacteria in hiding. Unforeseen, Bumann and his team uncovered an important teammate in the infection process, the protein EIIAGlc. The protein was already known for its many functions in bacterial metabolism, such as in the uptake of sugars molecules.
The researchers' attention was attracted by the fact that when EIIAGlc is defective Salmonella completely loses its capacity for intracellular replication and to spread throughout the organism. Further investigations finally brought the scientists from Basel onto the right track. The protein EIIAGlc docks onto the injection apparatus in the bacterium, stabilizes it and finally activates the release of the toxins. "We can clearly demonstrate that the activation of the secretion system is the main function of the protein EIIAGlc, while the many other described metabolic functions play a minor role in the occurrence of illness", says Bumann bringing his findings to the point.
Target molecule for antibiotic treatment
It is estimated that each year about 16 million people worldwide contract a life-threatening Salmonella infection that affects the whole organism. The spread of the bacteria in the host is highly dependent on the functional capacity of the injection system. "In EIIAGlc, we have found a new potential therapeutic target", says Bumann. By inhibiting the protein, one could strategically put the infection apparatus out of action. As this injection needle is primarily found in pathogens, infections could be effectively and specifically fought without harming the natural intestinal microflora.
###
Original source
Alain Mazé, Timo Glatter, Dirk Bumann
The central metabolism regulator EIIAGlc switches Salmonella from growth arrest to acute virulence through activation of virulence factor secretion Cell Reports, published online 15 May 2014 |
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Katrin Bühler
Copyright © University of Basel
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








