Home > Press > Engineers develop new materials for hydrogen storage
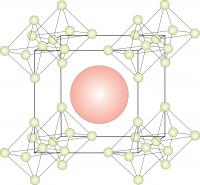 |
| The researchers have created for the first time compounds made from mixtures of calcium hexaboride, strontium and barium hexaboride. The resulting ceramics are essentially crystalline structures in a cage of boron. To store hydrogen, the researchers would swap the calcium, strontium and boron with hydrogen atoms within the cage.
Credit: Olivia Graeve/Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego |
Abstract:
Engineers at the University of California, San Diego, have created new ceramic materials that could be used to store hydrogen safely and efficiently.
Engineers develop new materials for hydrogen storage
San Diego, CA | Posted on April 15th, 2014The researchers have created for the first time compounds made from mixtures of calcium hexaboride, strontium and barium hexaboride. They also have demonstrated that the compounds could be manufactured using a simple, low-cost manufacturing method known as combustion synthesis.
The work is at the proof of concept stage and is part of a $1.2 million project funded by the National Science Foundation, a collaboration between UC San Diego, Alfred University in upstate New York and the University of Nevada, Reno. The manufacturing process for the ceramics is faster and simpler than traditional methods used to manufacture these types of materials. The researchers presented their work in March 2014 at the third International Symposium on Nanoscience and Nanomaterials in Mexico.
"We are looking for solid materials that can store and release hydrogen easily," said Olivia Graeve, a professor at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego, who has gained international recognition as a nanomaterials manufacturing expert. Storing hydrogen has become increasingly important as hydrogen fuel cells become more popular power sources in industry and elsewhere. But hydrogen, the lightest element on the periodic table, is difficult to store. It tends to diffuse through the walls of pressurized tanks. It also needs to be compressed in order to occupy manageable amounts of space when stored.
The resulting ceramics are essentially crystalline structures in a cage of boron. To store hydrogen, the researchers would swap the calcium, strontium and boron with hydrogen atoms within the cage.
Engineers mixed boron with metal nitrates and organic fuels, such as urea, in a box furnace at temperatures below 400 degrees Celsius—roughly 750 degrees Fahrenheit—cooler than a commercial pizza oven. The nitrates and organic fuels ignite, generating heat that then drives the reaction without the need for an external source of power. This method is known as combustion synthesis.
"It's a very simple, nice process," Graeve explained.
###
Graeve earned a bachelor's degree in structural engineering from UC San Diego in 1995 before earning a Ph.D. in materials science and engineering from the University of California, Davis in 2001. She was on faculty at the University of Nevada at Reno and Alfred University before joining UC San Diego in 2013.
Graduate student James Cahill will present the work at Research Expo, April 17, at the Jacobs School.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ioana Patringenaru
858-822-0899
Copyright © University of California - San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Events/Classes
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








