Home > Press > No compromises: JILA's short, flexible, reusable AFM probe
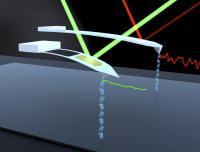 |
| This image shows JILA's modified AFM probes measuring DNA molecules. The older mod (long cantilever, right) eliminated the usual gold coating to enhance long-term stability. The latest version (left) retains the gold coating where needed to reflect light but maintains excellent stability. Researchers also removed a large section to reduce stiffness and friction near surfaces. The new probe provides precise results much faster than before, while reducing "noise" (colored squiggles).
Credit: Credit: Baxley/JILA |
Abstract:
JILA researchers have engineered a short, flexible, reusable probe for the atomic force microscope (AFM) that enables state-of-the-art precision and stability in picoscale force measurements. Shorter, softer and more agile than standard and recently enhanced AFM probes, the JILA tips will benefit nanotechnology and studies of folding and stretching in biomolecules such as proteins and DNA.
No compromises: JILA's short, flexible, reusable AFM probe
Posted on April 9th, 2014An AFM probe is a cantilever, shaped like a tiny diving board with a small, atomic-scale point on the free end. To measure forces at the molecular scale in a liquid, the probe attaches its tip to a molecule such as a protein and pulls; the resulting deflection of the cantilever is measured. The forces are in the realm of piconewtons, or trillionths of a newton. One newton is roughly the weight of a small apple.
The new probe design, described in ACS Nano,* is the JILA research group's third recent advance in AFM technology. JILA is jointly operated by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and University of Colorado Boulder.
The group previously improved AFM position stability by using laser beams to sense motion** and removing the gold coating from long probe tips, or cantilevers, to enhance long-term force stability.*** However, removing the gold reduces the strength of the signal being measured, and using long cantilevers leads to other measurement problems such as slower response to dynamic events like protein unfolding.
The latest modification overcomes these and other issues, improving precision without loss of stability, speed, or sensitivity. JILA researchers used a focused ion beam to cut a hole in the center of a short commercial cantilever and thinned the remaining support structures, thereby reducing the cantilever's stiffness and friction near surfaces. The result is excellent long-term stability and improved short-term precision, respectively, in AFM force measurements.
JILA researchers also added a protective glass cap over the gold coating at the end of the cantilever to retain beneficial reflectivity, and then removed the remaining gold to gain force stability. The modified cantilever enables rapid, precise and stable force measurements across a broad range of operating frequencies.
"Previously, we had to average the Brownian (random) motion of our favorite cantilever for about 60 milliseconds to get a measurement that had a precision of 1 piconewton," JILA/NIST biophysicist Tom Perkins says. "Now, we can get the same precision in 1 millisecond or so."
JILA researchers demonstrated significant benefits for single molecule studies. For instance, the short, soft cantilevers can quickly measure abrupt changes in force when a protein unfolds. Protein folding is required for proper biological function and misfolding can lead to diseases such as Alzheimer's. The new cantilevers match the response of stiffer, unmodified cantilevers but with greater stability and precision. Force stability is crucial in this application because protein folding and unfolding rates are exponentially sensitive to tiny changes (smaller than 1 piconewton) in applied load. The new device also can track fleeting nanoscale events, including protein folding, over hundreds of seconds—much longer periods than previously possible. The new design should also be applicable to rapid probing of the mechanical properties of materials at the nanoscale.
Significantly, the new cantilevers are robust enough to be reused for multiple days. Moreover, JILA researchers say the new design is simple and inexpensive to make, and thus, suitable for routine use.
"Amazingly, this project was spearheaded by a talented undergraduate. We hope other groups with similarly talented students will adopt these cantilevers. We certainly are," Perkins said.
###
The research was supported by the National Science Foundation and NIST.
*M.S. Bull, R.M.A. Sullan, H. Li and T.T. Perkins. Improved single-molecule force spectroscopy using micromachined cantilevers. ACS Nano. Published online March 26,2014. DOI:10.1021/nn5010588
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Laura Ost
303-497-4880
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








