Home > Press > Nano-paper filter removes viruses
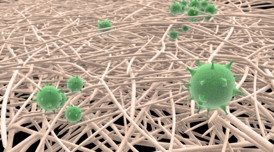 |
| The illustration shows the nanofibers in white and the virus in green.
Photograph: Björn Syse |
Abstract:
Nanotechnology and Functional Materials, Uppsala University have developed a paper filter, which can remove virus particles with the efficiency matching that of the best industrial virus filters. The paper filter consists of 100 percent high purity cellulose nanofibers, directly derived from nature.
Nano-paper filter removes viruses
Uppsala, Sweden | Posted on March 31st, 2014The research was carried out in collaboration with virologists from the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences/Swedish National Veterinary Institute and is published in the Advanced Healthcare Materials journal.
Virus particles are very peculiar objects- tiny (about thousand times thinner than a human hair) yet mighty. Viruses can only replicate in living cells but once the cells become infected the viruses can turn out to be extremely pathogenic. Viruses can actively cause diseases on their own or even transform healthy cells to malignant tumors.
"Viral contamination of biotechnological products is a serious challenge for production of therapeutic proteins and vaccines. Because of the small size, virus removal is a non-trivial task, and, therefore, inexpensive and robust virus removal filters are highly demanded" says Albert Mihranyan, Associate Professor at the Division of Nanotechnology and Functional Materials, Uppsala University, who heads the study.
Cellulose is one of the most common materials to produce various types of filters because it is inexpensive, disposable, inert and non-toxic. It is also mechanically strong, hydrophyllic, stable in a wide range of pH, and can withstand sterilization e.g. by autoclaving. Normal filter paper, used for chemistry, has too large pores to remove viruses.
The undergraduate student Linus Wågberg, Professor Maria Strømme, and Associate Professor Albert Mihranyan at the Division of Nanotechnology and Functional Materials, Uppsala University, in collaboration with virologists Dr. Giorgi Metreveli, Eva Emmoth, and Professor Sándor Belák from the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (SLU)/Swedish National Veterinary Institute (SVA), report a design of a paper filter which is capable of removing virus particles with the efficiency matching that of the best industrial virus filters. The reported paper filter, which is manufactured according to the traditional paper making processes, consists of 100 percent high purity cellulose nanofibers directly derived from nature.
The discovery is a result of a decade long research on the properties of high surface area nanocellulose materials, which eventually enabled the scientists to tailor the pore size distribution of their paper precisely in the range desirable for virus filtration.
Previously described virus removal paper filters relied heavily on interception of viruses via electrostatic interactions, which are sensitive to pH and salt concentrations, whereas the virus removal filters made from synthetic polymers and which rely on size-exclusion are produced through tedious multistep phase-inversion processing involving hazardous solvents and rigorous pore annealing processing.
Incidentally, it was the Swedish chemist J.J. Berzelius (1779-1848), one of the most famous alumni of Uppsala University, who was the first one to use the pure wet-laid-all-rag paper for separation of precipitates in chemical analysis. In a way, the virus removal nano-paper filter developed by the Uppsala scientists is the modern day analogue of the widely popular Swedish Filter Paper developed by Berzelius nearly two centuries ago.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Albert Mihranyan
46-701-679-037
Copyright © Uppsala University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The article is published in the Advanced Healthcare Materials journal on March 31, 2014:
The article is published in the Advanced Healthcare Materials journal on March 31, 2014:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








