Home > Press > Tiny Origami Boxes Hold Big Promise for Hydrogen Energy Storage: Graphene folds itself into programmable "nanocage" for hydrogen storage, beating DOE 2020 goal
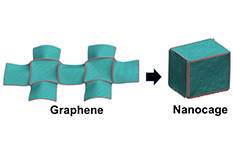 |
| A sheet of carbon atoms folds by applying water along the red lines, then can be used to store hydrogen atoms, say mechanical engineers at the University of Maryland. |
Abstract:
Just when you thought your origami skills couldn't be beat - try using the world's thinnest material, making the origami fold and unfold itself, and packing more inside than anyone expected. Researchers from the University of Maryland have done just that.
A sheet of carbon atoms folds itself into a box that opens and closes as an electric field is applied. This graphene "nanocage" could hold high densities of hydrogen for energy storage, say its inventors in the department of mechanical engineering at the University of Maryland.
Credit: Maryland NanoCenter
Tiny Origami Boxes Hold Big Promise for Hydrogen Energy Storage: Graphene folds itself into programmable "nanocage" for hydrogen storage, beating DOE 2020 goal
College Park, MD | Posted on March 12th, 2014Graphene is the world's thinnest material, just one atom thick. Mechanical engineers Shuze Zhu and Teng Li have found that they can make tiny squares of graphene fold into a box, which will open and close itself in response to an electric charge.
Inside the box, they've tucked hydrogen atoms, and have done so more efficiently than was thought possible. The U.S. Department of Energy is searching for ways to make storing energy with hydrogen a practical possibility, and they set up some goals: by 2017, the Department had hoped that a research team could pack in 5.5 percent hydrogen by weight, and that by 2020, it could be stretched to 7.5 percent.
Li's team has already crossed that threshold, with a hydrogen storage density of 9.5 percent hydrogen by weight. The team has also demonstrated the potential to reach an even higher density, a future research goal.
"Just like paper origami that can make complicated 3-D structures from 2-D paper, graphene origami allows us to design and fabricate carbon nanostructures that are not naturally existing but of desirable properties," said Li. "We have made nano-baskets, as well as these new nano-cages to hold hydrogen and other molecular cargos."
The U.S. National Science Foundation supported the team's research, which will be published in the journal ACS Nano.
####
About University of Maryland
The University of Maryland is the state's flagship university and one of the nation's preeminent public research universities. A global leader in research, entrepreneurship and innovation, the university is home to more than 37,000 students, 9,000 faculty and staff, and 250 academic programs. Its faculty includes three Nobel laureates, two Pulitzer Prize winners, 49 members of the national academies and scores of Fulbright scholars. The institution has a $1.8 billion operating budget, secures $500 million annually in external research funding and recently completed a $1 billion dollar fundraising campaign.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Martha Heil
301-405-0876
Maryland Nanocenter
University of Maryland
Copyright © University of Maryland
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








