Home > Press > UC research tests which nano system works best in killing cancer cells: New UC research to be presented this week tested four iron-oxide nanoparticle systems to see which, when heated, would likely work best as a tool for targeting cancer cells
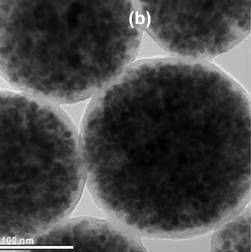 |
| View of iron-oxide nanoparticles embedded in a polystyrene matrix as seen via a transmission electron microscope. These nanoparticles, when heated, can be applied to cancer cells in order to kill those cells. |
Abstract:
In current research related to improving cancer treatments, one promising area of research is the effort to find ways to selectively pinpoint and target cancer cells while minimizing effects on healthy cells.
UC research tests which nano system works best in killing cancer cells: New UC research to be presented this week tested four iron-oxide nanoparticle systems to see which, when heated, would likely work best as a tool for targeting cancer cells
Cincinnati, OH | Posted on March 4th, 2014In that effort, it's already been found in lab experiments that iron-oxide nanoparticles, when heated and then applied specifically to cancer cells, can kill those cells because cancer cells are particularly susceptible to changes in temperature. Increasing the temperature of cancer cells to over 43 degrees Celsius (about 109 degrees Fahrenheit) for a sufficient period of time can kill those cells.
So, a University of Cincinnati-led team - along with researchers at Iowa State University, the University of Michigan and Shanghai Jiao Tong University - recently conducted experiments to see which iron-oxide nanoparticle configurations or arrangements might work best as a tool to deliver this killing heat directly to cancer cells, specifically to breast cancer cells. The results will be presented at the March 3-7 American Physical Society Conference in Denver by UC physics doctoral student Md Ehsan Sadat.
In systematically studying four distinct magnetized nanoparticle systems with different structural and magnetic properties, the research team found that an unconfined nanoparticle system, which used an electromagnetic field to generate heat, was best able to transfer heat absorbed by cancer cells.
So, from the set of nano systems studied, the researchers found that uncoated iron-oxide nanoparticles and iron-oxide nanoparticles coated with polyacrylic acid (PAA) - both of which were unconfined or not embedded in a matrix - heated quickly and to temperatures more than sufficient to kill cancer cells.
Uncoated iron-oxide nanoparticles increased from a room temperature of 22 degrees Celsius to 66 degrees Celsius (about 150 degrees Fahrenheit).
Iron-oxide nanoparticles coated with polyacrylic acid (PAA) heated from a room temperature of 22 degrees Celsius to 73 degrees Celsius (about 163 degrees Fahrenheit.)
The goal was to determine the heating behaviors of different iron-oxide nanoparticles that varied in terms of the materials used in the nanoparticle apparatus as well as particle size, particle geometry, inter-particle spacing, physical confinement and surrounding environment since these are the key factors that strongly influence what's called the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), or the measured rate at which the human body can absorb energy (in this case heat) when exposed to an electromagnetic field.
According to Sadat, "What we found was that the size of the particles and their anisotropic (directional) properties strongly affected the magnetic heating achieved. In other words, the smaller the particles and the greater their directional uniformity along an axis, the greater the heating that was achieved."
He added the systems' heating behaviors were also influenced by the concentrations of nanoparticles present. The higher the concentration of nanoparticles (the greater the number of nanoparticles and the more densely collected), the lower the SAR or the rate at which the tissue was able to absorb the heat generated.
THE FOUR SYSTEMS STUDIED
The researchers studied
uncoated iron-oxide nanoparticles
iron-oxide nanoparticles coated with polyacrylic acid (PAA)
a polystyrene nanosphere with iron-oxide nanoparticles uniformly embedded in its matrix
a polystyrene nanosphere with iron-oxide nanoparticles uniformly embedded in its matrix but with a thin film surface of silica
All four nanoparticle systems were exposed to the same magnetic field for 35 minutes, and temperature measurements were performed at two-minute intervals.
As stated, the PAA iron-oxide and the uncoated iron-oxide samples showed the highest temperature change. The lowest temperature changes, insufficient to kill cancer cells, were exhibited by
The polystyrene nanosphere, which heated to 36 degrees Celsius (about 96 degree Fahrenheit).
The polystyrene nanosphere with a silica coating heated to 40 degrees Celsius (104 degrees Fahrenheit).
In addition to Sadat, others on the research team include Ronak Patel, former master's student in materials sciences and engineering in UC's College of Engineering and Applied Science; Jason Sookoor, undergraduate neuroscience student from UC's McMicken College of Arts and Sciences; Sergey L. Bud'ko, adjunct associate professor, Ames Laboratory and Department of Physics and Astronomy, Iowa State University; Rodney C. Ewing, Edward H. Kraus distinguished university professor, University of Michigan; Jiaming Zhang, assistant research scientist, University of Michigan; Hong Xu of the Med-X Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong University; Giovanni M. Pauletti, associate professor in UC's James L. Winkle College of Pharmacy; David B. Mast, associate professor of physics in UC's McMicken College of Arts and Sciences; and Donglu Shi, professor of materials science and engineering at UC's College of Engineering and Applied Science.
Support for this research was provided by a National Science Foundation grant under contract number NSF (1343568) titled "Development of Nanotechnology Minor Focused on Nano Biomedicine and Sustainable Energy." Work at the Ames Laboratory was supported by the United States Department of Energy, Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
M.B. Reilly
513-556-1824
Copyright © University of Cincinnati
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Events/Classes
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks January 20th, 2023
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








