Home > Press > Silver nanoparticle on graphene oxide support: An efficient catalyst for organic transformations
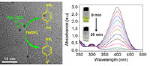 |
| Figure 1: (Left) Transmission electron microscopy image of Ag-rGO nanohybrids. The inset shows the catalytic conversion of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol. Figure 2 (Right) Absorption spectra of 4-nitrophenol decreases in intensity and its color fades (inset) due to catalytic conversion. |
Abstract:
Silver (Ag) has a high catalytic activity towards many organic and inorganic transformations such as NOx reduction and catalytic oxidation of CO to CO2. In practical applications, catalysts like Ag are affixed to a substrate, usually a solid with a high surface area such as alumina or carbon.
Silver nanoparticle on graphene oxide support: An efficient catalyst for organic transformations
Toyohashi, Japan | Posted on March 2nd, 2014To efficiently use Ag as a catalyst, its specific surface area must be maximized by reducing its particle size. Moreover, the development of simple and low-cost synthesis method is highly desired for practical applications.
Now, Tran Viet Thu and colleagues at Toyohashi University of Technology have shown that graphene oxide (GO) sheets can be used as an excellent support for the growth of Ag particles. GO was first prepared from commercial graphite by oxidation and exfoliation in water. Then the Ag-GO hybrids were prepared by a chemical reduction route using GO and silver nitrate as precursors, sodium borohydride as reducing agent, and trisodium citrate as stabilizer.
Transmission electron microscopy imaging showed very small size (3.6±0.6 nm) Ag particles to be decorated on GO sheets, compared with Ag particles synthesized without GO (tens of nm in size). This decrease in particle size means more Ag atoms were present at the surface and a large increase in the specific surface area. As a result, the Ag-GO hybrids were more efficient for the catalytic conversion of 4-nitrophenol (toxic pollutant) into 4-aminophenol, an intermediate for the production of several drugs. In addition, the Ag-GO hybrids exhibited improved catalytic activity compared to Ag particles synthesized without GO.
The research suggests a low-cost route for the synthesis of catalytic Ag-GO hybrids and highlights the promising use of GO as a support for other functional nanostructures.
Reference:
Authors: Tran Viet Thu, Pil Ju Ko, Nguyen Huu Huy Phuc, and Adarsh Sandhu.
Title of original paper: Room-temperature synthesis and enhanced catalytic performance of silver-reduced graphene oxide nanohybrids.
Journal, volume, pages and year: Journal of Nanoparticle Research 15 (10), 1-13 (2013).
Digital Object Identifier (DOI): 10.1007/s11051-013-1975-9
Affiliations: Electronics-Inspired Interdisciplinary Research Institute (EIIRIS) and Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Toyohashi University of Technology, 1-1 Hibarigaoka, Tempaku, Toyohashi, Aichi Prefecture, 441-8580, JAPAN
Enquiries
Toyohashi University of Technology, International Affairs Division
TEL: +81-532-44-6577
or +81-532-44-6546
Copyright © Toyohashi University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
![]() Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
Single-atom catalysts change spin state when boosted by a magnetic field June 4th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








