Home > Press > Now in 3-D: Video of virus-sized particle trying to enter cell
 |
Abstract:
Tiny and swift, viruses are hard to capture on video. Now researchers at Princeton University have achieved an unprecedented look at a virus-like particle as it tries to break into and infect a cell. The technique they developed could help scientists learn more about how to deliver drugs via nanoparticles — which are about the same size as viruses — as well as how to prevent viral infection from occurring.
Now in 3-D: Video of virus-sized particle trying to enter cell
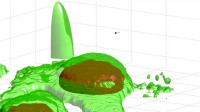
Princeton, NJ | Posted on February 24th, 2014The video reveals a virus-like particle zipping around in a rapid, erratic manner until it encounters a cell, bounces and skids along the surface, and either lifts offagain or, in much less time than it takes to blink an eye, slips into the cell's interior. The work was published in Nature Nanotechnology.
"The challenge in imaging these events is that viruses and nanoparticles are small and fast, while cells are relatively large and immobile," said Kevin Welsher, a postdoctoral researcher in Princeton's Department of Chemistry and first author on the study. "That has made it very hard to capture these interactions."
The problem can be compared to shooting video of a hummingbird as it roams around a vast garden, said Haw Yang, associate professor of chemistry and Welsher's adviser. Focus the camera on the fast-moving hummingbird, and the background will be blurred. Focus on the background, and the bird will be blurred.
The researchers solved the problem by using two cameras, one that locked onto the virus-like nanoparticle and followed it faithfully, and another that filmed the cell and surrounding environment.
Putting the two images together yielded a level of detail about the movement of nano-sized particles that has never before been achieved, Yang said. Prior to this work, he said, the only way to see small objects at a similar resolution was to use a technique called electron microscopy, which requires killing the cell.
"What Kevin has done that is really different is that he can capture a three-dimensional view of a virus-sized particle attacking a living cell, whereas electron microscopy is in two-dimensions and on dead cells," Yang said. "This gives us a completely new level of understanding."
In addition to simply viewing the particle's antics, the researchers can use the technique to map the contours of the cell surface, which is bumpy with proteins that push up from beneath the surface. By following the particle's movement along the surface of the cell, the researchers were able to map the protrusions, just as a blind person might use his or her fingers to construct an image of a person's face.
"Following the motion of the particle allowed us to trace very fine structures with a precision of about 10 nanometers, which typically is only available with an electron microscope," Welsher said. (A nanometer is one billionth of a meter and roughly 1000 times smaller than the width of a human hair.) He added that measuring changes in the speed of the particle allowed the researchers to infer the viscosity of the extracellular environment just above the cell surface.
The technology has potential benefits for both drug discovery and basic scientific discovery, Yang said. "We believe this will impact the study of how nanoparticles can deliver medicines to cells, potentially leading to some new lines of defense in antiviral therapies," he said. "For basic research, there are a number of questions that can now be explored, such as how a cell surface receptor interacts with a viral particle or with a drug."
Welsher added that such basic research could lead to new strategies for keeping viruses from entering cells in the first place.
"If we understand what is happening to the virus before it gets to your cells," said Welsher, "then we can think about ways to prevent infection altogether. It is like deflecting missiles before they get there rather than trying to control the damage once you've been hit."
To create the virus-like particle, the researchers coated a miniscule polystyrene ball with quantum dots, which are semiconductor bits that emit light and allow the camera to find the particle. Next, the particle was studded with protein segments known as Tat peptides, derived from the HIV-1 virus, which help the particle find the cell. The width of the final particle was about 100 nanometers.
The researchers then let loose the particles into a dish containing skin cells known as fibroblasts. One camera followed the particle while a second imaging system took pictures of the cell using a technique called laser scanning microscopy, which involves taking multiple images, each in a slightly different focal plane, and combining them to make a three-dimensional picture.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Catherine Zandonella
Copyright © Princeton University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Video - Virus-Like Particle Attacking Cell:
Video - Virus-Like Particle Attacking Cell:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








