Home > Press > NIST microanalysis technique makes the most of small nanoparticle samples
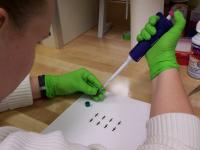 |
| Small piezoelectric quartz crystals are the key to micro thermogavimetric analysis. Here, minute amounts of the test sample are deposited on the crystals.
Credit: Kar/National Institute of Standards and Technology |
Abstract:
Researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have demonstrated that they can make sensitive chemical analyses of minute samples of nanoparticles by, essentially, roasting them on top of a quartz crystal. The NIST-developed technique, "microscale thermogravimetric analysis," holds promise for studying nanomaterials in biology and the environment, where sample sizes often are quite small and larger-scale analysis won't work.*
NIST microanalysis technique makes the most of small nanoparticle samples
Gaithersburg, MD | Posted on February 24th, 2014Chemical analysis of nanoparticles is a challenging task, and not just because they're small. They're also complicated. They can become coated with other materials in their environment, and the question becomes, what materials? Or they might have been engineered with a coating, perhaps to provide anchor points for drug molecules, and then the question can be, how complete is the coating? In nanoelectronics, the question may be, how pure is the sample and just what are the impurities?
Researchers have an alphabetic array of tools for this, including scanning, transmission or atomic force microscopy (SEM/TEM/AFM); dynamic light scattering (DLS); nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); and sundry spectrometry techniques, but they all have a variety of limitations, including complex sample preparation or the difficulty of analyzing enough particles to get a statistically significant result.
On the other hand, one technique, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) is quite straight-forward. The sample is heated and monitored for changes in mass as the temperature increases. Sudden changes in mass correlate with the energies needed to decompose, oxidize, dehydrate or otherwise chemically change components in the sample. If you have some idea of what you start with, TGA can tell you much more, but it requires pretty substantial sample sizes.
NIST's technique is essentially the same except that a small piezoelectric quartz crystal is substituted for the mass scale. A tiny amount of a nanomaterial sample deposited on the crystal dampens the crystal's resonant frequency, and as the sample grows lighter, the frequency shifts. NIST researchers originally applied it to measure the purity of carbon nanotube samples.**
In this latest paper, the research team tested the utility of microTGA on typical nanomaterial analysis problems, including assessing the purity of carbon nanotubes, determining the amount of surface-bound ligands (i.e., molecular anchors) on gold nanoparticles, and testing for the presence of PEG, a polymer commonly used in medicine on silicon oxide nanoparticles.
"Our results are a pretty close match to other techniques," reports NIST analytical chemist Elisabeth Mansfield, "but using far less of a sample."
In fact, the team reports, microTGA gets results using samples a thousand times smaller than conventional techniques. It can work with one microgram of sample and detect mass changes of less than a nanogram. "That's important because you often don't have much of a sample.," Mansfield says," If you're pulling nanoparticles out of a water sample from the environment to measure how much exists in a real world sample, you're going to have very little to work with."
"In nanomedicine, the surface chemistry is oftentimes critically important to the performance of the nanomaterial," notes FDA chemist Katherine Tyner. "When working with real life samples, we may only have a very small sample amount. MicroTGA allows us to obtain information that we otherwise would not be able to get with conventional techniques."
###
*E. Mansfield , K.M. Tyner, C.M. Poling and J.L. Blacklock. Determination of nanoparticle tsurface coatings and nanoparticle purity using microscale thermogravimetric analysis. Anal. Chem., 2014, 86 (3), pp 1478-1484 DOI: 10.1021/ac402888v.
####
About National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Commerce.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Baum
301-975-2763
Copyright © National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
A battery’s hopping ions remember where they’ve been: Seen in atomic detail, the seemingly smooth flow of ions through a battery’s electrolyte is surprisingly complicated February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








