Home > Press > Gecko-inspired Adhesion: Self-cleaning and Reliable
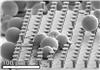 |
| Glass spheres among microhairs that are mushroom-shaped to improve adhesive force. SEM: Michael Röhrig, KIT |
Abstract:
Geckos outclass adhesive tapes in one respect: Even after repeated contact with dirt and dust do their feet perfectly adhere to smooth surfaces. Researchers of the KIT and the Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, have now developed the first adhesive tape that does not only adhere to a surface as reliably as the toes of a gecko, but also possesses similar self-cleaning properties. Using such a tape, food packagings or bandages might be opened and closed several times. The results are published in the "Interface" journal of the British Royal Society. DOI: rsif.2013.1205
Gecko-inspired Adhesion: Self-cleaning and Reliable
Karlsruhe, Germany | Posted on February 20th, 2014When moving forwards, the gecko‘s toes drag across a part of the surface. As a result of this lateral friction contact, larger dirt particles are removed. Smaller particles deposit among the setae on the sole and in the skinfolds below. In an experiment, the researchers have proved that both mechanisms provide for 95% of the self-cleaning effect. "This effect is determined by the ratio between particle size and setae diameter", Dr. Hendrik Hölscher of KIT's Institute of Microstructure Technology (IMT) says.
For their experiments, the scientists used elastic microhairs of variable size. Instead of dirt particles, they employed glass spheres of micrometer size (10-6 meters) and distributed them on a smooth plate. To simulate the steps made by a gecko, they pressed an artificial adhesive tape covered by microhairs onto the plate, shifted it laterally, and lifted the tape off again. This "load-drag-unload" cycle was repeated several times. In parallel, adhesive force was measured.
When the diameter of the spheres exceeded that of the microhairs, the adhesive force disappeared after the first contact ("load") - as in case of an ordinary adhesive tape. After eight to ten test cycles, however, the gecko-inspired adhesive tape reached 80 to 100 percent of its original power again. "In the long term, this effect might be used to develop a low-cost alternative to hook and loop fasteners," Hölscher says. "Such a tape might be applied in the sports sector, in medicine, automotive industry or aerospace technology," Metin Sitti, Professor of the Carnegie Mellon University, adds.
When the size of the spheres was smaller than the diameter of the microhairs, the researchers succeeded in restoring one third of the original adhesive force only. "For the perfect gecko-inspired adhesive tape, we therefore need fibers in the nanometer range (10-9 meters), which are smaller than most dirt particles", Dr. Michael Röhrig, IMT scientist, emphasizes. The skinfolds of the gecko have already been reproduced by wide grooves between narrow rows of hair. They offer enough space for the fine dust to deposit. Tests using real dirt particles of variable shape and size and particles made of various materials are planned to be carried out in the near future.
####
About Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
The Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is the merger of the Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, member of the Helmholtz Association, and the Universität Karlsruhe. This merger will give rise to an institution of internationally excellent research and teaching in natural and engineering sciences. In total, the KIT has 8000 employees and an annual budget of 700 million Euros. The KIT focuses on the knowledge triangle of research – teaching – innovation.
The Karlsruhe institution is a leading European energy research center and plays a visible role in nanosciences worldwide. KIT sets new standards in teaching and promotion of young scientists and attracts top scientists from all over the world. Moreover, KIT is a leading innovation partner of industry.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Monika Landgraf
Karlsruhe Institut of Technology
+49 721 608 47414
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








