Home > Press > Nanofriction on the tip of the microscope: A new research paper from SISSA published in Nature Materials
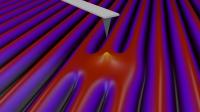 |
| This is a graphical rendering of the "system" studied by Pellegrini, Santoro, Tosatti.
Credit: SISSA |
Abstract:
Atomic force microscopes are able to reproduce spectacular images, at the scale of single atoms. This is made possible by the oscillation of a very sharp probe tip over the surface being observed. The tip never touches the surface but gets so close to it, at distances in the order of one billionth of a metre, that it "feels" the force due to the interaction with the atoms making up the material being observed. These are tiny forces, in the order of nanonewtons (meaning one billion times smaller than the weight of an apple). By measuring these forces one can reproduce an image of the material. A research group, which brings together experimental physicists from the University of Basel and theoretical physicists from SISSA, has observed and explained a peculiar effect, a source of "friction" in this type of nanoscopic observations.
Nanofriction on the tip of the microscope: A new research paper from SISSA published in Nature Materials
Trieste, Italy | Posted on December 16th, 2013When the tip of the microscope oscillates over certain surfaces, in this case over NbSe2 (niobium selenide), peaks of "dissipation" (i.e., loss of energy) can be seen when the tip is at specific distances from the surface, as if it were held back, at certain locations, by some frictional force. This effect, which is related to a property of the surface known as charge density waves (CDW), was experimentally observed by the Basel physicists and first explained by Franco Pellegrini, Giuseppe Santoro and Erio Tosatti, of SISSA, by means of a theoretical model analysed with the use of numerical simulations.
"Our model describes in detail the interaction between the tip of the atomic force microscope and the CDW," explains Pellegrini. "The model reproduces - and predicts - the data observed experimentally".
"Knowledge of nanofriction is important today. Progressive miniaturization of electronic devices makes it crucial to understand the mechanisms underlying energy losses", continues Pellegrini. "In addition, thanks to our work we now have a more accurate description of charge density waves". The paper was published on December 15 in Nature Materials.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Federica Sgorbissa
39-040-378-7644
Copyright © International School of Advanced Studies (SISSA)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








