Home > Press > Scientists scale terahertz peaks in nanotubes: Rice U. researchers find plasmonic root of terahertz signals in some carbon nanotubes
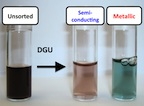 |
| The ability to sort carbon nanotubes by type through a process called “density gradient ultracentrifugation (DGU)” allowed Rice researchers to test purified batches of nanotubes to find the cause of terahertz peaks in spectroscopic experiments. They determined that free electrons formed plasmons that ripple at terahertz frequencies in metallic and doped nanotubes. Credit: Kono Laboratory/Rice University |
Abstract:
Carbon nanotubes carry plasmonic signals in the terahertz range of the electromagnetic spectrum, but only if they're metallic by nature or doped.
Scientists scale terahertz peaks in nanotubes: Rice U. researchers find plasmonic root of terahertz signals in some carbon nanotubes
Houston, TX | Posted on December 9th, 2013In new research, the Rice University laboratory of physicist Junichiro Kono disproved previous theories that dominant terahertz response comes from narrow-gap semiconducting nanotubes.
Knowing that metallic or doped nanotubes respond with plasmonic waves at terahertz frequencies opens up the possibility that the tubes can be used in a wide array of optoelectronic amplifiers, detectors, polarizers and antennas.
The work by Kono and his Rice colleagues appeared online recently in the American Chemical Society journal Nano Letters.
Scientists have long been aware of a terahertz peak in nanotubes, the tiny cylinders of rolled-up carbon that show so much promise for advanced materials. But experiments on batches of nanotubes, which generally grow in a willy-nilly array of types, failed to reveal why it was there.
The origin of the peak was not explainable because researchers were only able to experiment on mixed batches of nanotube types, said Qi Zhang, a graduate student in Kono's group and lead author of the paper. "All the previous work was done with a mixture of semiconducting and metallic tubes. We are the first to clearly identify the plasmonic nature of this terahertz response," he said.
Rice's growing expertise in separating nanotubes by type allowed Kono and his group to test for terahertz peaks in batches of pure metallic nanotubes known as "armchairs" as well as nonmetallic, semiconducting tubes.
"Metallic carbon nanotubes are expected to show plasmon resonance in the terahertz and infrared range, but no group has clearly demonstrated the existence of plasmons in carbon nanotubes," Zhang said. "Previously, people proposed one possible explanation -- that the terahertz peak is due to interband absorption in the small band gaps in semiconducting nanotubes. We rejected that in this paper."
Plasmons are free electrons on the surface of metals like gold, silver or even aluminum nanoparticles that, when triggered by a laser or other outside energy, ripple like waves in a pond. Strong waves can trigger plasmon responses in adjacent nanoparticles. They are being investigated at Rice and elsewhere for use in sophisticated electronic and medical applications.
The Kono group's research showed plasmons rippling at terahertz frequencies only along the length of a nanotube, but not across its width. "The only way charge carriers can move around is in the long direction," Kono said. The researchers previously used this fact to demonstrate that aligned carbon nanotubes act as an excellent terahertz polarizer with performance better than commercial polarizers based on metallic grids.
Nanotubes can be thousands of times longer than they are wide, and the ability to grow them (or cut them) to specific lengths or to dope semiconducting nanotubes to add free carriers would make the tubes highly tunable for terahertz frequencies, Kono said.
"This paper only clarifies the origin of this effect," he said. "Now that we understand it, there's so much to do. We will be making various terahertz devices, architectures and systems based on carbon nanotube plasmons."
Rice alumni Erik Hároz, now a postdoctoral researcher at Los Alamos National Laboratory, and Lei Ren, a researcher at TGS, co-authored the paper with undergraduate student Zehua Jin, postdoctoral researcher Xuan Wang, senior research scientist Rolf Arvidson and Andreas Lüttge, a research professor of Earth science and chemistry, all of Rice. Kono is a professor of electrical and computer engineering and of physics and astronomy and of materials science and nanoengineering.
The Department of Energy, the National Science Foundation and the Robert A. Welch Foundation supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to tinyurl.com/AboutRiceU.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








