Home > Press > Infrared vision lets researchers see through — and into — multiple layers of graphene
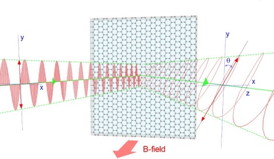 |
| The direction that a light wave is oscillating changes as the wave is reflected by a sheet of graphene. Researchers exploited this changing quality to identify the electronic properties of multiple sheets of graphene stacked atop one another even when they were covering each other up. Credit: Chul Soo Kim, U.S. Naval Research Laboratory |
Abstract:
It's not X-ray vision, but you could call it infrared vision.
A University at Buffalo-led research team has developed a technique for "seeing through" a stack of graphene sheets to identify and describe the electronic properties of each individual sheet — even when the sheets are covering each other up.
Infrared vision lets researchers see through — and into — multiple layers of graphene
Buffalo, NY | Posted on November 21st, 2013The method involves shooting a beam of infrared light at the stack, and measuring how the light wave's direction of oscillation changes as it bounces off the layers within.
To explain further: When a magnetic field is applied and increased, different types of graphene alter the direction of oscillation, or polarization, in different ways. A graphene layer stacked neatly on top of another will have a different effect on polarization than a graphene layer that is messily stacked.
"By measuring the polarization of reflected light from graphene in a magnetic field and using new analysis techniques, we have developed an ultrasensitive fingerprinting tool that is capable of identifying and characterizing different graphene multilayers," said John Cerne, PhD, UB associate professor of physics, who led the project.
The technique allows the researchers to examine dozens of individual layers within a stack.
Graphene, a nanomaterial that consists of a single layer of carbon atoms, has generated huge interest due to its remarkable fundamental properties and technological applications. It's lightweight but also one of the world's strongest materials. So incredible are its characteristics that it garnered a Nobel Prize in Physics in 2010 for two scientists who pioneered its study.
Cerne's new research looks at graphene's electronic properties, which change as sheets of the material are stacked on top of one another. The findings appeared Nov. 5 in Scientific Reports, an online, open-access journal produced by the publishers of Nature.
Cerne's collaborators included colleagues from UB and the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory.
So, why don't all graphene layers affect the polarization of light the same way?
Cerne says the answer lies in the fact that different layers absorb and emit light in different ways.
The study showed that absorption and emission patterns change when a magnetic field is applied, which means that scientists can turn the polarization of light on and off either by applying a magnetic field to graphene layers or, more quickly, by applying a voltage that sends electrons flowing through the graphene.
"Applying a voltage would allow for fast modulation, which opens up the possibility for new optical devices using graphene for communications, imaging and signal processing," said first author Chase T. Ellis, a former graduate research assistant at UB and current postdoctoral fellow at the Naval Research Laboratory.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Charlotte Hsu
Media Relations Manager, Architecture, Economic Development, Sciences, Urban and Regional Planning
Tel: 716-645-4655
Twitter: @UBScience
Pinterest: UB Science
Copyright © University at Buffalo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








