Home > Press > Nanogrid, activated by sunlight, breaks down pollutants in water, leaving biodegradable compounds: Innovation Corps project explores how to bring technology to the field
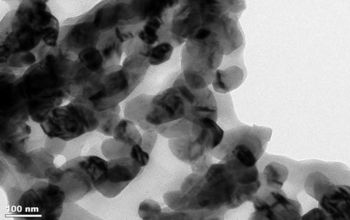 |
| Transmission electron microscopy image and related electron diffraction pattern of the nanogrids structures as manifested at the nanoparticle level. Each nanoparticle is about 20nm and it is connected to the next one forming "links" in a chain-like configuration.
Credit: Perena Gouma, CNSD, SUNY Stony Brook |
Abstract:
Oil spills do untold damage to the environment--to the waters they pollute and to marine and other wildlife. The Deepwater Horizon spill in the Gulf of Mexico in 2010, for example, the largest accidental marine oil spill in the history of the petroleum industry, flowed unabated for three months.
Nanogrid, activated by sunlight, breaks down pollutants in water, leaving biodegradable compounds: Innovation Corps project explores how to bring technology to the field
Arlington, VA | Posted on November 9th, 2013Typically, such oil spills are extraordinarily difficult to clean up.
Soon, however, the process may become infinitely easier and ecologically friendly, the result of a new invention by a National Science Foundation- (NSF) supported scientist.
Pelagia-Irene (Perena) Gouma, a professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at the State University of New York (SUNY) Stony Brook, created a novel "nanogrid," a large net consisting of metal grids made of a copper tungsten oxide, that, when activated by sunlight, can break down oil from a spill, leaving only biodegradable compounds behind.
"We have made a new catalyst that can break down hydrocarbons in water, and it does not contaminate the water," says Gouma, who also directs SUNY's Center for Nanomaterials and Sensor Development. "It utilizes the whole solar spectrum and can work in water for a long time, which no existing photocatalyst can do now. Ours is a unique technology. When you shine light on these grids, they begin to work and can be used over and over again.
"Something like this would work fine for any oil spill," Gouma adds. "Any ship can carry them, so if they have even a small amount of spill, they can take care of it."
Initially, the grids, which resemble non-woven mats of miniaturized ceramic fishing nets, probably will be used for oil spills, although they potentially could prove valuable in other applications, such as cleaning contaminated water produced by "fracking," the process of hydraulic fracturing to extract natural gas from shale, and as well as from other industrial processes.
"Fracking is a reality," she says. "It is happening. If the science and engineering we produce in the lab can help alleviate environmental problems, we will be happy about that."
Because they work well both in water and air, they also could be a chemical-free, possibly even water-free, method of cleaning clothes in the future. "The dry cleaning process that we now use involves a lot of contaminants that have to be remediated and treated, such as benzene," she says. "This could be a dry cleaning substitute that would be more environmentally friendly than current dry cleaning approaches."
Moreover, "imagine you lay this over your clothes, and expose them to light. You won't need a washing machine, or chemicals, or even water," she adds.
The photocatalytic nanogrids™ invented in her lab are made by a unique self-assembly process that occurs "during the nanomanufacturing on non-woven nanofibrous mats deposited on metal meshes," according to Gouma. "Upon heating, metal clusters diffuse inside polymeric nanofibers, then turn into single crystal nanowires, then oxidize to form metal oxide--ceramic--nanoparticles that are interconnected, like links in a chain," she says.
These form an unusual and "robust third architecture that allows for the highest surface area, providing maximum exposure to the contaminant to be remediated, while the nanoscale particle sizes enable fast catalytic action," she adds. "The result is a self-supported water remediation targeted photocatalytic technology that has no precedent."
In the fall of 2011, Gouma was the first scientist to receive a $50,000 NSF Innovation Corps (I-Corps) award, which supports a set of activities and programs that prepare scientists and engineers to extend their focus beyond the laboratory into the commercial world.
Such results may be translated through I-Corps into technologies with near-term benefits for the economy and society. It is a public-private partnership program that teaches grantees to identify valuable product opportunities that can emerge from academic research, and offers entrepreneurship training to faculty and student participants.
"The I-Corps program was very useful for the students," she says. "It got them involved, and got them to realize that there is a practical application to what they do. It was extremely useful for them to see how something developed in the lab could be used in the field, and that you actually can start a business from something started in the lab."
She and her team are in the process of creating a startup business--they have two patents pending on the process--with the hope of scaling up production and carrying out pilot studies.
"We want to demonstrate feasibility in the real world, and then produce them in large quantities," she says. "We have proof of principle that our technology can be useful. Our technique works in the lab. We now need to make sure that it works in the field."
-- Marlene Cimons, National Science Foundation
####
About National Science Foundation (NSF)
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent federal agency that supports fundamental research and education across all fields of science and engineering. In fiscal year (FY) 2012, its budget was $7.0 billion. NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 colleges, universities and other institutions. Each year, NSF receives about 50,000 competitive requests for funding, and makes about 11,500 new funding awards. NSF also awards about $593 million in professional and service contracts yearly.
For more information, please click here
Copyright © National Science Foundation (NSF)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Dr. Perena Gouma's Center for Nanomaterials and Sensor Development:
Dr. Perena Gouma's Center for Nanomaterials and Sensor Development:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








