Home > Press > A chameleon in the physics lab: Looking cooler when heated, a thin coating tricks infrared cameras
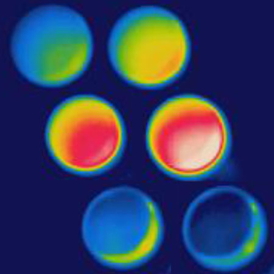 |
| A new coating intrinsically conceals its own temperature to thermal cameras. Image courtesy of Mikhail Kats. |
Abstract:
Active camouflage has taken a step forward at the Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS), with a new coating that intrinsically conceals its own temperature to thermal cameras.
A chameleon in the physics lab: Looking cooler when heated, a thin coating tricks infrared cameras
Cambridge, MA | Posted on October 22nd, 2013In a laboratory test, a team of applied physicists placed the device on a hot plate and watched it through an infrared camera as the temperature rose. Initially, it behaved as expected, giving off more infrared light as the sample was heated: at 60 degrees Celsius it appeared blue-green to the camera; by 70 degrees it was red and yellow. At 74 degrees it turned a deep red—and then something strange happened. The thermal radiation plummeted. At 80 degrees it looked blue, as if it could be 60 degrees, and at 85 it looked even colder. Moreover, the effect was reversible and repeatable, many times over.
These surprising results, published today in the journal Physical Review X (an open-access publication of the American Physical Society), illustrate the potential for a new class of engineered materials to contribute to a range of new military and everyday applications.
Principal investigator Federico Capasso, Robert L. Wallace Professor of Applied Physics and Vinton Hayes Senior Research Fellow in Electrical Engineering at Harvard SEAS, predicts that with only small adjustments the coating could be used as a new type of thermal camouflage or as a kind of encrypted beacon to allow soldiers to covertly communicate their locations in the field.
The secret to the technology lies within a very thin film of vanadium oxide, an unusual material that undergoes dramatic electronic changes when it reaches a particular temperature. At room temperature, for example, pure vanadium oxide is electrically insulating, but at slightly higher temperatures it transitions to a metallic, electrically conductive state. During that transition, the optical properties change, too, which means special temperature-dependent effects—like infrared camouflage—can also be achieved.
The insulator-metal transition has been recognized in vanadium oxide since 1959. However, it is a difficult material to work with: in bulk crystals, the stress of the transition often causes cracks to develop and can shatter the sample. Recent advances in materials synthesis and characterization—especially those by coauthor Shriram Ramanathan, Associate Professor of Materials Science at Harvard SEAS—have allowed the creation of extremely pure samples of thin-film vanadium oxide, enabling a burst of new science and engineering to take off in just the last few years.
"Thanks to these very stable samples that we're getting from Prof. Ramanathan's lab, we now know that if we introduce small changes to the material, we can dramatically change the optical phenomena we observe," explains lead author Mikhail Kats, a graduate student in Capasso's group at Harvard SEAS. "By introducing impurities or defects in a controlled way via processes known as doping, modifying, or straining the material, it is possible to create a wide range of interesting, important, and predictable behaviors."
By doping vanadium oxide with tungsten, for example, the transition temperature can be brought down to room temperature, and the range of temperatures over which the strange thermal radiation effect occurs can be widened. Tailoring the material properties like this, with specific outcomes in mind, may enable engineering to advance in new directions.
The researchers say a vehicle coated in vanadium oxide tiles could potentially mimic its environment like a chameleon, appearing invisible to an infrared camera with only very slight adjustments to the tiles' actual temperature—a far more efficient system than the approaches in use today.
Tuned differently, the material could become a component of a secret beacon, displaying a particular thermal signature on cue to an infrared surveillance camera. Capasso's team suggests that the material could be engineered to operate at specific wavelengths, enabling simultaneous use by many individually identifiable soldiers.
And, because thermal radiation carries heat, the researchers believe a similar effect could be employed to deliberately speed up or slow down the cooling of structures ranging from houses to satellites.
The Harvard team's most significant contribution is the discovery that nanoscale structures that appear naturally in the transition region of vanadium oxide can be used to provide a special level of tunability, which can be used to suppress thermal radiation as the temperature rises. The researchers refer to such a spontaneously structured material as a "natural, disordered metamaterial."
"To artificially create such a useful three-dimensional structure within a material is extremely difficult," says Capasso. "Here, nature is giving us what we want for free. By taking these natural metamaterials and manipulating them to have all the properties we want, we are opening up a new area of research, a completely new direction of work. We can engineer new devices from the bottom up."
This work was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and by a graduate research fellowship from the National Science Foundation. In addition to Capasso, Kats, and Ramanathan, coauthors included research associate Patrice Genevet and graduate students Romain Blanchard, Shuyan Zhang, and Changhyun Ko, all at Harvard SEAS.
About Physical Review X
Launched in August 2011, PRX (prx.aps.org) is an open-access, peer-reviewed publication of the American Physical Society (www.aps.org), a non-profit membership organization working to advance and diffuse the knowledge of physics through its outstanding research journals, scientific meetings, and education, outreach, advocacy and international activities. APS represents 50,000 members, including physicists in academia, national laboratories and industry in the United States and throughout the world.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Caroline Perry
617-496-1351
Copyright © Harvard School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








