Home > Press > ORNL superconducting wire yields unprecedented performance
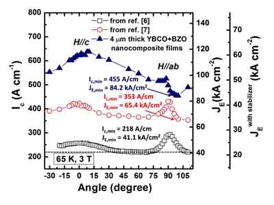 |
| This figure shows the critical current, Ic, and engineering critical current density, JE, in a superconducting wire as a function of applied magnetic field orientation at 65 Kelvin and 3 Tesla. The top curve shows results from a newly published ORNL study. The other two curves are from previously reported record values. A minimum JE of 43.7 kiloamperes/cm2 (assuming a 50 micron thick stabilizer layer) and a minimum Ic of 455 Amperes/cm was obtained for all applied field orientations. This is the highest reported performance for a superconductor wire or a film on a technical substrate. |
Abstract:
The ability to control nanoscale imperfections in superconducting wires results in materials with unparalleled and customized performance, according to a new study from the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
ORNL superconducting wire yields unprecedented performance
Oak Ridge, TN | Posted on August 16th, 2013Applications for superconducting wires, which carry electricity without resistance when cooled to a critical temperature, include underground transmission cables, transformers and large-scale motors and generators. But these applications require wires to operate under different temperature and magnetic field regimes.
A team led by ORNL's Amit Goyal demonstrated that superconducting wires can be tuned to match different operating conditions by introducing small amounts of non-superconducting material that influences how the overall material behaves. Manipulating these nanoscale columns -- also known as defects -- allows researchers to exert control over the forces that regulate the wires' superconducting performance. The team's findings are published in Nature Publishing Group's Scientific Reports.
"Not only can we introduce these nanocolumn defects within the superconductor and get enhanced performance, but we can optimize the performance for different application regimes by modifying the defect spacing and density," Goyal said.
A wire sample grown with this process exhibited unprecedented performance in terms of engineering critical current density, which measures the amount of current the wire can carry per unit cross-sectional area. This metric more accurately reflects the real-world capabilities of the material because it takes into account the wire's non-superconducting components such as the substrate and the buffer and stabilizer layers, Goyal said.
"We report a record performance at 65 Kelvin and 3 Tesla, where most rotating machinery applications like motors and generators are slated to operate," he said.
The paper reports a minimum engineering critical current density at all applied magnetic field orientations of 43.7 kiloamperes/cm2, which is more than twice the performance level needed for most applications. This metric assumes the presence of a 50-micron-thick copper stabilizer layer required in applications.
Generating defects in the superconductor is accomplished through an ORNL-developed self-assembly process, which enables researchers to design a material that automatically develops the desired nanoscale microstructure during growth.
The mechanism behind this process, which adds very little to the production cost, was the subject of a recently published study by a team led by Goyal in Advanced Functional Materials.
"When you're making the wires, you can dial-in the properties because the defects self-assemble," Goyal said. "You change the composition of the superconductor when you're depositing the tape."
Goyal, who has collaborated with multiple superconducting technology companies, hopes the private sector will incorporate the team's findings to improve upon existing products and generate new applications.
The study is published as "Engineering nanocolumnar defect configurations for optimized vortex pinning in high temperature superconducting nanocomposite wires." Co-authors are ORNL's Sung Hun Wee and Claudia Cantoni and the University of Tennessee's Yuri Zuev.
The research was sponsored by DOE's Office of Electricity Delivery and Energy Reliability. The research was supported by ORNL's Shared Research Equipment (ShaRE) User Program, which is sponsored by DOE's Office of Science.
####
About Oak Ridge National Laboratory
ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle for the Department of Energy's Office of Science. DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Morgan McCorkle
865-574-7308
Copyright © Oak Ridge National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor April 25th, 2025
Lattice-driven charge density wave fluctuations far above the transition temperature in Kagome superconductor April 25th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








