Home > Press > Rice technique expands options for molecular imaging: One-of-a-kind spectrometer reads vibrations between atoms to find structures of molecules
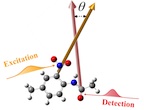 |
| A technique by Rice University chemist Junrong Zheng measures vibrations between atoms to determine the three-dimensional form of molecules. Credit: Zheng Lab/Rice University |
Abstract:
-- A Rice University laboratory has improved upon its ability to determine molecular structures in three dimensions in ways that challenge long-used standards.
Rice technique expands options for molecular imaging: One-of-a-kind spectrometer reads vibrations between atoms to find structures of molecules
Houston, TX | Posted on August 15th, 2013By measuring the vibrations between atoms using femtosecond-long laser pulses, the Rice lab of chemist Junrong Zheng is able to discern the positions of atoms within molecules without the restrictions imposed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging.
The technique can capture the structure of molecules at room temperature or very low or high temperatures and in many kinds of samples, including crystals, powders, gels, liquids and gases. It will be useful to scientists who study catalysis, energy storage, organic solar cells and biomembranes, among many other possibilities, Zheng said.
The researchers reported their results online this week in the American Chemical Society's Journal of Physical Chemistry.
Zheng and his co-authors at Rice and Oak Ridge National Laboratory analyzed variations of a model molecule, 4'-methyl-2'nitroacetanilide (MNA), and compared the results with computer-generated and XRD models. The images matched nicely, he said.
Traditional spectrometers read the wavelengths of light scattered by samples to identify materials and study their properties. But the one-of-a-kind spectrometer developed by Zheng uses very short laser pulses to read the vibrational energies inherent to every atom. Those energies determine how atoms bond to form a molecule, and a measurement of the length and angles of those bonds can be extracted from the vibrations themselves, he said.
The infrared and terahertz lasers used for the experiment captured information about a molecular angle in a mere 100 femtoseconds. (One femtosecond is a millionth of a billionth of a second.)
"The important part of this paper is to demonstrate that our method can determine three-dimensional molecular structures no matter whether they're in liquids or solids," Zheng said.
"Typically, when organic chemists synthesize a molecule, they know its makeup but have no idea what the structure is," he said. "Their first option is to make a single crystal of the molecule and use XRD to determine the precise structure. But in many cases it's very tedious, if not impossible, to grow a single crystal.
"People also use NMR to learn the structure," he said. "But the trouble with many molecules is the solubility is really bad. Insoluble molecules can't be read well by either method."
The Rice technique, dubbed "multiple-dimensional vibrational spectroscopy," is able to capture the conformation of small molecules -- for starters -- with great accuracy, Zheng said. The spectrometer reads only intramolecular interactions among vibrations and ignores interactions between molecules, he said.
"The atoms in every molecule are always vibrating, and each bond between atoms vibrates at a certain frequency, and in a certain direction," he said. "We found that if we can measure the direction of one vibration and then another, then we can know the angle between these two vibrations - and therefore the angle between the bonds."
He said the researchers begin with the chemical formula and already know, through Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, how many vibrational frequencies are contained in a given molecule. "Then we measure each vibrational mode, one by one. Once we get all the cross-angles, we can translate this to a model," he said.
For now, as a proof of concept, Zheng and his team analyze molecules for which the structure is already known. Over time, the technique should be able to analyze much larger molecules, like viruses that contain thousands or tens of thousands of atoms, he said.
"This is just the first demonstration that this method works," he said. "These are simple molecules, 23 or 24 atoms. I think it will take some time to get to proteins. My expectation is that it will take 10 to 20 years to develop. Remember, for NMR, it took 50 years to be able to read the structure of proteins."
Hailong Chen, a Welch postdoctoral research fellow at Rice, is lead author of the paper; Co-authors are Rice graduate students Yufan Zhang and Jiebo Li and Oak Ridge researchers Hongjun Liu and De-en Jiang. Zheng is an assistant professor of chemistry.
The Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the Welch Foundation, the Packard Foundation and the Department of Energy supported the research.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 2 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to tinyurl.com/AboutRiceU.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Jade Boyd
713-348-6778
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








