Home > Press > Molecules form 2-D patterns never before observed: Nanoscience experiments produce elusive 5-vertex tilings
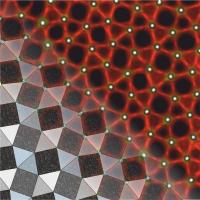 |
| The 2-D tessellation pattern known as the "semiregular snub square tiling" stands out clearly in this image, which combines scanning tunneling microscopy with computer graphics. The pattern, observed in a surface architecture just one molecule thick, was formed by self-assembly of linear organic linkers, imaged as rods, and lanthanide cerium centers, visualized as bright protrusions. The area shown measures less than 25 nanometers across.
Credit: Barth Lab, copyright TUM |
Abstract:
Tessellation patterns that have fascinated mathematicians since Johannes Kepler worked out their systematics 400 years ago - and that more recently have caught the eye of both artists and crystallographers - can now be seen in the laboratory. They first took shape on a surface more perfectly two-dimensional than any sheet of writing paper, a single layer of atoms and molecules atop an atomically smooth substrate. Physicists coaxed these so-called Kepler tilings "onto the page" through guided self-assembly of nanostructures.
Molecules form 2-D patterns never before observed: Nanoscience experiments produce elusive 5-vertex tilings
Munich, Germany | Posted on August 8th, 2013The experiments were carried out by postdoctoral researcher David Ecija, PhD candidate Jose Ignacio Urgel and colleagues in the Physics Department of Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM), in collaboration with scientists in Karlsruhe and Zurich. They reported their findings in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Results open a new line of research
Organic molecules equipped with functional groups to express distinct linkages to metal atoms were deposited onto a smooth silver substrate under vacuum conditions. Subsequently the organic layer on this platform was exposed to an atomic flux of the lanthanide cerium. At a certain ratio of cerium atoms to molecules, self-assembly produced a symmetrical complex 2-D pattern described originally by Kepler and known today as the snub square tiling. Clearly identifiable through scanning tunneling microscopy was a recurring, five-vertex connecting element less than one nanometer across, a cerium-ligand coordination unit.
That the snub square tiling pattern had never been fabricated and seen at the molecular level by exploiting self-assembly protocols was interesting in itself. Beyond that, the physicists explain, every new surface architecture could potentially open the way to novel physics and chemistry, and until now five-vertex structures have proven elusive. In particular, the fact that the lanthanide element cerium played such a key role marks this as the beginning of a new line of research.
This is the first time the TUM researchers - members of Prof. Johannes Barth's Institute for Molecular Nanoscience and Chemical Physics of Interfaces - have coordinated molecules with a lanthanide, and the first time anyone has done this in 2-D. "And lanthanides are special," David Ecija explains. "They have very intriguing optical, magnetic, and chemical properties that could be interesting for nanoscience, and possibly also for nanotechnology. Now we have a new playground for research with the lanthanides, and beyond."
This research was supported by the European Research Council through Advanced Grant MolArt (Grant 247299) and Marie Curie Fellowship Grant 274842; the German Research Foundation (DFG) through Grant BA3395/2-1; and the TUM Institute for Advanced Study.
Publication
Five-vertex Archimedean surface tessellation by lanthanide-directed molecular self-assembly. David Ecija, Jose I. Urgel, Anthoula C. Papageorgiou, Sushobhan Joshi, Willi Auwaerter, Ari P. Seitsonen, Svetlana Klyatskaya, Mario Ruben, Sybille Fischer, Saranyan Vijayaraghavan, Joachim Reichert, and Johannes V. Barth. PNAS 2013 Vol. 110 No. 17, pp. 6678-6681. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1222713110
####
About Technische Universitaet Muenchen
Technische Universitaet Muenchen (TUM) is one of Europe's leading universities. It has roughly 500 professors, 9,000 academic and non-academic staff, and 32,000 students. It focuses on the engineering sciences, natural sciences, life sciences, medicine, and economic sciences. After winning numerous awards, it was selected as an "Excellence University" in 2006 and 2012 by the Science Council (Wissenschaftsrat) and the German Research Foundation (DFG). In both international and national rankings, TUM is rated as one of Germany's top universities. TUM is dedicated to the ideal of a top-level research-oriented entrepreneurial university. The university's global presence includes offices in Beijing (China), Brussels (Belgium), Cairo (Egypt) and Sao Paulo (Brazil). The German Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), founded in 2002 in Singapore, is the first research campus of a German university abroad.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ecija
Dept. of Physics
Technische Universitaet Muenchen
James-Franck-Str. 1
85748 Munich, Germany
T: +49 89 289 12320
E:
W: http://www.e20.ph.tum.de/
Patrick Regan
49-016-242-79876
Technische Universitaet Muenchen
Copyright © Technische Universitaet Muenchen
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








