Home > Press > VCU Physicists Discover Theoretical Possibility of Large, Hollow Magnetic Cage Molecules: New molecules could be larger than the original Buckminster fullerene with potential applications in technology and health care
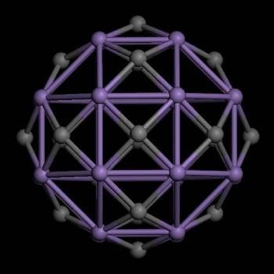 |
| Illustration depicts a Mn24C18 cluster carrying a magnetic moment of 70 Bohr magnetons. Image courtesy of Menghao Wu, Ph.D./VCU. |
Abstract:
Virginia Commonwealth University researchers have discovered, in theory, the possibility of creating large, hollow magnetic cage molecules that could one day be used in medicine as a drug delivery system to non-invasively treat tumors, and in other emerging technologies.
VCU Physicists Discover Theoretical Possibility of Large, Hollow Magnetic Cage Molecules: New molecules could be larger than the original Buckminster fullerene with potential applications in technology and health care
Richmond, VA | Posted on July 31st, 2013Approximately 25 years ago, scientists first made the discovery of C60 fullerene - better known as the Buckminster Fullerene - a molecule composed of 60 carbon molecules that formed a hollow cage. Due to its unique hollow cage structure the molecule offers serious technological potential because it could hold other atoms or small molecules inside, and therefore, be used in applications such as drug delivery.
That potential has since spurred worldwide interest among scientists who have been searching for similar molecules. Although some hollow cage structures have been found, none of them is magnetic. Magnetic properties of the structure are of particular interest because a hollow magnetic structure carrying an embedded atom or molecule can be guided by an external magnetic field and may serve as an effective vehicle for targeted drug delivery.
In a new study, published online on July 22 in The Journal of Chemical Physics, two VCU scientists employing state-of-the-art theoretical methods show that magnetic hollow cages larger than the original C60 fullerene that carry giant magnetic moments are possible. A magnetic moment refers to the measure of the magnetic strength of a cluster.
An illustration of the VCU discovery also is featured on the cover of the July 28 print issue of the journal.
"The potential benefit of this finding is that it provides a route to the synthesis of molecular magnets with colossal magnetic moments," said co-lead investigator Puru Jena, Ph.D., distinguished professor of physics in the VCU College of Humanities and Sciences. Jena collaborated with Menghao Wu, Ph.D., co-author of the paper and a postdoctoral scholar in the VCU Department of Physics.
"These molecules can be used for targeted non-invasive drug delivery. When assembled, the molecules can also form new high strength magnets for device application," Jena said.
According to Jena, the pair of VCU researchers demonstrated the magnetic moment of the molecule by focusing on hetero-atomic clusters consisting of transition metal atoms such as cobalt (Co) and manganese (Mn) and carbon (C) atoms. In particular, Co12C6, Mn12C6, and Mn24C18 clusters consisting of 12 cobalt and six carbon atoms, 12 manganese and six carbon atoms, and 24 manganese and 18 carbon atoms, respectively, carry magnetic moments as large as 14, 38 and 70 Bohr magnetons. In comparison, the magnetic moment of an iron (Fe) atom in crystalline iron is 2.2 Bohr magnetons.
According to Jena, the team is still early in its discovery process.
"There is a long way to go. Experiments first have to be carried out to prove the predictions of our theory," said Jena.
"Ways must be found to synthesize large quantities of these molecules and study their magnetic properties once they are assembled. Finally, these molecules need to be functionalized by embedding desired atoms/molecules for practical applications."
This research was supported in part by the U.S. Department of Energy grant number DE-FG02-96ER45579.
####
About Virginia Commonwealth University
Virginia Commonwealth University is a major, urban public research university with national and international rankings in sponsored research. Located in downtown Richmond, VCU enrolls more than 31,000 students in 223 degree and certificate programs in the arts, sciences and humanities. Sixty-eight of the programs are unique in Virginia, many of them crossing the disciplines of VCU’s 13 schools and one college. MCV Hospitals and the health sciences schools of Virginia Commonwealth University comprise the VCU Medical Center, one of the nation’s leading academic medical centers.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sathya Achia Abraham
804-828-1231
Copyright © Virginia Commonwealth University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The study is titled, “Magnetic hollow cages with colossal moments.”:
The study is titled, “Magnetic hollow cages with colossal moments.”:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








