Home > Press > Elementary Physics in a Single Molecule
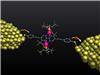 |
| The molecule of about 2 nm in size is kept stable between two metal electrodes for several days. Figure: Christian Grupe/KIT |
Abstract:
A team of physicists has succeeded in performing an extraordinary experiment: They demonstrated how magnetism that generally manifests itself by a force between two magnetized objects acts within a single molecule. This discovery is of high significance to fundamental research and provides scientists with a new tool to better understand magnetism as an elementary phenomenon of physics. The researchers published their results in the latest issue of Nature Nanotechnology (doi: 10.1038/nnano.2013.133).
Elementary Physics in a Single Molecule
Karlsruhe, Germany | Posted on July 25th, 2013The smallest unit of a magnet is the magnetic moment of a single atom or ion. If two of these magnetic moments are coupled, two options result: Either the magnetic moments add up to a stronger moment or they compensate each other and magnetism disappears. From the quantum physics point of view, this is referred to as a triplet or singlet. A team of researchers around Professor Mario Ruben from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and Professor Heiko B. Weber from the Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg now wanted to find out whether the magnetism of a pair of magnetic moments can be measured electrically in a single molecule.
For this purpose, the team headed by Mario Ruben used a customized molecule of two cobalt ions for the experiment. At Erlangen, Heiko B. Weber and his team studied the molecule in a so-called single-molecule junction. This means that two metal electrodes are arranged very closely to each other, such that the molecule of about 2 nm in length is kept stable between these electrodes for many days, while current through the junction can be measured. This experimental setup was then exposed to various, down to very deep, temperatures. The scientists found that magnetism can be measured in this way. The magnetic state in the molecule became visible as Kondo anomaly. This is an effect that makes electric resistance shrink towards deep temperatures.
It occurs only when magnetism is active and, hence, may be used as evidence. At the same time, the researchers succeeded in switching this Kondo effect on and off via the applied voltage. A precise theoretical analysis by the group of Assistant Professor Karin Fink from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology determines the various complex quantum states of the cobalt ion pair in more detail. Hence, the researchers succeeded in reproducing elementary physics in a single molecule.
Full bibliographic information
Switching of a coupled spin pair in a single-molecule junction, Stefan Wagner et al., Nature Nanotechnology (2013), doi: 10.1038/nnano.2013.133.
####
About Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
The Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) is the merger of the Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, member of the Helmholtz Association, and the Universität Karlsruhe. This merger will give rise to an institution of internationally excellent research and teaching in natural and engineering sciences. In total, the KIT has 8000 employees and an annual budget of 700 million Euros. The KIT focuses on the knowledge triangle of research – teaching – innovation.
The Karlsruhe institution is a leading European energy research center and plays a visible role in nanosciences worldwide. KIT sets new standards in teaching and promotion of young scientists and attracts top scientists from all over the world. Moreover, KIT is a leading innovation partner of industry.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Monika Landgraf
Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
+49 721 608 47414
Copyright © AlphaGalileo
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








