Home > Press > Efficient Production Process for Coveted Nanocrystals
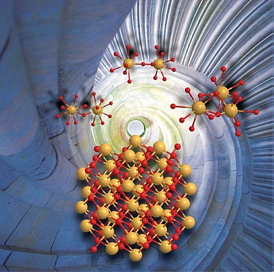 |
| Ce(IV) dimers and trimers form in aqueous solution nanometer-sized cer dioxide crystals (CeO2). The size of the nanocrystals is in the order of two to three nanometers. Picture: A. Ikeda-Ohno |
Abstract:
A formation mechanism of nanocrystalline cerium dioxide (CeO2), a versatile nanomaterial, has been unveiled by scientists from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) and the University of New South Wales in Sydney, Australia. The research results were published in the scientific journal Chemistry - A European Journal (DOI: 10.1002/chem.201204101). This finding potentially simplifies and alleviates the existing synthetic processes of nanocrystalline CeO2 production.
Efficient Production Process for Coveted Nanocrystals
Dresden, Germany and Sydney, Australia | Posted on June 25th, 2013Nanocrystalline CeO2 particles are widely used, for example, in catalysts for hazardous gas treatment, in electrodes for solid oxide fuel cells, in polishing materials for advanced integrated circuits, in sunscreen cosmetics, and in such medical applications as artificial superoxide dismutase. Current industrial syntheses of nanocrystalline CeO2 are based on sol-gel processes followed by thermal treatment and/or the addition of accelerant reagents. Any further improvement of the synthetic strategy for CeO2 nanocrystals requires a better understanding of the mechanisms involved in their formation at the atomic scale.
Dr. Atsushi Ikeda-Ohno from the University of New South Wales, Australia, together with Dr. Christoph Hennig from the HZDR opted for a sophisticated multi-spectroscopic approach that combines dynamic light scattering and synchrotron-based X-ray techniques. These complex investigations involved the use of two world-leading synchrotron facilities of the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility (ESRF) in Grenoble, France and SPring-8 in Hyogo, Japan.
Live Monitoring
For the first time ever, the scientists were able to perform an in-situ observation of nanocrystal evolution. So far, little has been known of the formation mechanism of metal nanocrystals; mainly because appropriate analytical techniques were lacking. The most widely used techniques for metal nanocrystal research are electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. They are powerful enough to visualize the appearance of nanocrystals and to acquire their lattice information, but they are not applicable to the solution state where the evolution of metal nanocrystals occurs. "To probe the formation of nanocrystalline CeO2 in an aqueous solution, we combined different spectroscopic techniques, including dynamic light scattering, synchrotron X-ray absorption spectroscopy, and high energy X-ray scattering," says Dr. Atsushi Ikeda-Ohno.
The information the researchers obtained is fundamental to simplifying and alleviating the synthetic process of CeO2 nanocrystals. They revealed that uniformly sized nanoparticles of CeO2 can be produced simply by pH adjustment of tetravalent cerium (Ce(IV)) in an aqueous solution without subsequent physical/chemical treatment such as heating or adding accelerant chemicals. The produced CeO2 crystals have a uniform particle size of 2 - 3 nanometers, irrespective of the preparation conditions (e.g. pH and type of pH adjustment). This particle size is exactly in the range which is interesting for industrial applications. A key finding is that mononuclear Ce(IV) solution species do not result in nano-sized CeO2 crystals. The prerequisite is the presence of oligomeric Ce(IV) solution species, such as dimers or trimers.
"We're indeed very glad that our multi-spectroscopic approach is also applicable to any other research on metal nanocrystals. That's why this study contributes to an emerging research area on metal nanocrystals in a broader context," says Dr. Christoph Hennig. "And the HZDR's own measuring station at the ESRF provides the best possible opportunities for this research area of metal nanocrystals which directly contributes to industrial applications."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Dr. Vinzenz Brendler | Dr. Christoph Hennig
Institute of Resource Ecology at the HZDR
Rossendorf Beamline at the ESRF/Grenoble
Phone: +49 351 260 - 3210 | +33 476 88 - 2005
Dr. Atsushi Ikeda-Ohno
School of Civil and Environmental Engineering
The University of New South Wales
UNSW, Sydney, New South Wales 2052, Australia
Phone: +61 2 9385 0128
Contact to the Media
Dr. Christine Bohnet
49-351-260-2450
Copyright © Helmholtz Association of German Research Centres
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








