Home > Press > Gold nanocrystal vibration captured on billion-frames-per-second film
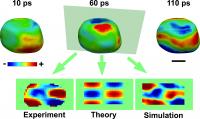 |
| The acoustic phonons can be visualized on the surface as regions of contraction (blue) and expansion (red). Also shown are two-dimensional images comparing the experimental results with theory and molecular dynamics simulation. The scale bar is 100 nanometers.
Credit: Jesse Clark/UCL |
Abstract:
A billon-frames-per-second film has captured the vibrations of gold nanocrystals in stunning detail for the first time.
Gold nanocrystal vibration captured on billion-frames-per-second film
London, UK | Posted on May 23rd, 2013The film, which was made using 3D imaging pioneered at the London Centre for Nanotechnology (LCN) at UCL, reveals important information about the composition of gold. The findings are published in the journal Science.
Jesse Clark, from the LCN and lead author of the paper said: "Just as the sound quality of a musical instrument can provide great detail about its construction, so too can the vibrations seen in materials provide important information about their composition and functions."
"It is absolutely amazing that we are able to capture snapshots of these nanoscale motions and create movies of these processes. This information is crucial to understanding the response of materials after perturbation. "
Scientists found that the vibrations were unusual because they start off at exactly the same moment everywhere inside the crystal. It was previously expected that the effects of the excitation would travel across the gold nanocrystal at the speed of sound, but they were found to be much faster, i.e., supersonic.
The new images support theoretical models for light interaction with metals, where energy is first transferred to electrons, which are able to short-circuit the much slower motion of the atoms.
The team carried out the experiments at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory using a revolutionary X-ray laser called the "Linac Coherent Light Source". The pulses of X-rays are extremely short (measured in femtoseconds, or quadrillionths of a second), meaning they are able to freeze all motion of the atoms in any sample, leaving only the electrons still moving.
However, the X-ray pulses are intense enough that the team was able to take single snapshots of the vibrations of the gold nanocrystals they were examining. The vibration was started with a short pulse of infrared light.
The vibrations were imaged a short time later in 3D using the coherent diffraction imaging methods pioneered in LCN by the Robinson group. The 3D movies reveal in exquisite detail the distortions taking place within the nanocrystal, with the fastest vibrations repeating every 90 picoseconds.
Professor Robinson, also from the LCN and the group leader, said: "This work represents an impressive example of teamwork by about a hundred people at SLAC. The SLAC linear accelerator was built in 1957 in direct response to the news of Sputnik.
"After compelling 50 years of sensational high energy physics, that machine has been refitted as a laser by the addition of a 100m long array of magnets. This 3km-sized machine produces a beam which is focused onto a crystal smaller than a micron in a pulse so short that all motion of its atoms is frozen still."
The research team included contributors from UCL, University of Oxford, SLAC, Argonne National Laboratory and LaTrobe University, Australia.
####
About University College London
Founded in 1826, UCL was the first English university established after Oxford and Cambridge, the first to admit students regardless of race, class, religion or gender and the first to provide systematic teaching of law, architecture and medicine.
We are among the world's top universities, as reflected by our performance in a range of international rankings and tables. According to the Thomson Scientific Citation Index, UCL is the second most highly cited European university and the 15th most highly cited in the world.
UCL has nearly 25,000 students from 150 countries and more than 9,000 employees, of whom one third are from outside the UK. The university is based in Bloomsbury in the heart of London, but also has two international campuses – UCL Australia and UCL Qatar. Our annual income is more than £800 million.
www.ucl.ac.uk | Follow us on Twitter @uclnews | Watch our YouTube channel YouTube.com/UCLTV
About the London Centre for Nanotechnology
The London Centre for Nanotechnology is a UK-based multidisciplinary enterprise operating at the forefront of science and technology. Its purpose is to solve global problems in information processing, healthcare, energy and environment through the application of nanoscience and nanotechnology. Founded in 2003, the LCN is a joint venture between UCL (University College London) and Imperial College London. www.london-nano.com
About the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC)
SLAC is a multi-program laboratory exploring frontier questions in photon science, astrophysics, particle physics and accelerator research. Located in Menlo Park, California, SLAC is operated by Stanford University for the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science. To learn more, please visit www.slac.stanford.edu
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit www.science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Clare Ryan
44-020-310-83846
Copyright © University College London
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








