Home > Press > Atomic-Scale Investigations Solve Key Puzzle of LED Efficiency: MIT and Brookhaven Lab scientists use electron microscopy imaging techniques to settle a solid-state controversy and raise new experimental possibilities
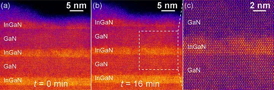 |
| These images of the InGaN samples—produced by CFN's low-voltage scanning transmission electron microscope—reveal a lack of structural changes over time. After 16 minutes of scanning, no damage or decomposition is visible, and the higher magnification (c) exhibits none of the clustering previously theorized to be central to LED efficiency. |
Abstract:
From the high-resolution glow of flat screen televisions to light bulbs that last for years, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) continue to transform technology. The celebrated efficiency and versatility of LEDs-and other solid-state technologies including laser diodes and solar photovoltaics-make them increasingly popular. Their full potential, however, remains untapped, in part because the semiconductor alloys that make these devices work continue to puzzle scientists.
Atomic-Scale Investigations Solve Key Puzzle of LED Efficiency: MIT and Brookhaven Lab scientists use electron microscopy imaging techniques to settle a solid-state controversy and raise new experimental possibilities
Upton, NY | Posted on May 22nd, 2013A contentious controversy surrounds the high intensity of one leading LED semiconductor-indium gallium nitride (InGaN)-with experts split on whether or not indium-rich clusters within the material provide the LED's remarkable efficiency. Now, researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have demonstrated definitively that clustering is not the source. The results-published online May 16 in Applied Physics Letters-advance fundamental understanding of LED technology and open new research pathways.
"This discovery helps solve a significant mystery in the field of LED research and demonstrates breakthrough experimental techniques that can advance other sensitive and cutting-edge electronics," said Silvija Gradecak, the Thomas Lord Associate Professor of Materials Science and Engineering at MIT and a coauthor on the study. "The work brings us closer to truly mastering solid-state technologies that could supply light and energy with unprecedented efficiency."
Building a Better Bulb
Incandescent lights-the classic bulbs that use glowing wires of tungsten or other metals-convert only about five percent of their energy into visible light, with the rest lost as heat. Fluorescent lights push that efficiency up to about 20 percent, still wasting 80 percent of the electricity needed to keep homes and businesses bright. In both of these instances, light is only the byproduct of heat-generating reactions rather than the principal effect, making the technology inherently inefficient.
"Solid-state lights convert electric current directly into photons," said Eric Stach, leader of the Electron Microscopy Group at Brookhaven Lab's Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN) and a co-author on the study. "LED bulbs use semiconductors to generate light in a process called electroluminescence. The efficiency of this process could, in theory, be nearly perfect, but the experimental realization has not reached those levels. That disconnect helped motivate this study."
For this study, the scientists looked at the LED compound InGaN (pronounced in-gan), which is particularly promising for practical applications. InGaN alloys contain dislocations-structural imperfections that could inhibit electricity flow and light production-but somehow the alloy performs exceptionally well. To understand the light-emitting reactions, physicists needed to understand what was happening on the atomic scale. After researchers started to investigate, however, not everyone reached the same conclusions.
Controversial Clusters
"Years ago, a team of researchers used electron microscopes to examine InGaN samples, and they identified a surprising phenomenon-the material appeared to be spontaneously decomposing and forming these isolated indium-rich clusters," Stach said. "This behavior could explain the efficient light emission, as the clusters might help electrons avoid the structural problems in the InGaN. But then things became really interesting when another group proposed that the electron microscope itself caused that clustering decomposition. We had a real divide in the semiconductor field."
Rather than using light to examine materials, electron microscopes bombard samples with finely tuned beams of electrons and detect their interactions when they pass through a sample to reveal atomic structures. To achieve high enough resolution to examine the InGaN alloys, the electron microscopes used in the older experiments needed high-voltage beams. The controversy revolved around whether or not the experiment itself produced the clusters, rather than discovering the mechanism behind efficient light emission.
Improved Imaging
"The state-of-the-art instruments available at Brookhaven Lab's CFN changed the way we could test these promising materials," Gradecak said. "The CFN's aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) opened a new and non-destructive window into the LED samples. For the first time, we could get Ångstrom-level details-that's one tenth of one nanometer-without the risk of the device affecting the sample."
The researchers combined the leading STEM techniques with high-resolution electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS), which measured the energy lost by electrons as they passed through the sample. Post-doctoral researchers Kamal Baloch of MIT-the lead author of the study-and Aaron Johnston-Peck of CFN actually applied these imaging techniques to the same samples that first launched the controversy over clustering, helping further settle the issue.
"We found that the indium-rich clusters do not actually exist in these samples, even though they remain efficient light emitters," Baloch said. "While clustering may still occur in other samples, which may be prepared in different ways, the important point is that we've established a foolproof method for investigating InGaN materials. We can use these non-destructive imaging techniques to explore the fundamental relationship between cluster formation and light emission to help unlock the secrets of this amazing alloy."
Beyond the advanced imaging instruments, researchers used the expertise of Brookhaven Lab physicist Kim Kisslinger, who specializes in nanoscale sample preparation. The InGaN samples were reduced to a thickness of just 20 nanometers, an essential step in priming the materials for STEM and EELS experimentation. The samples were also painstakingly cleaned and polished to eliminate artifacts that might impact image resolution.
The research was supported by the Center for Excitonics, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. The work at Brookhaven Lab's Center for Functional Nanomaterials was also supported by DOE's Office of Science, with additional work carried out at the MIT Center for Materials Science Engineering.
"The Center for Excitonics gave us the freedom and funding to look at this fundamental question, knowing that these explorations will ultimately push the limits of LED technology," Gradecak said. "This was a strong collaboration between MIT and Brookhaven's CFN, demonstrating the concentration of expertise and instrumentation that really pushes science and technology forward."
The Center for Functional Nanomaterials is one of the five DOE Nanoscale Science Research Centers, premier national user facilities for interdisciplinary research at the nanoscale supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science. Together the NSRCs comprise a suite of complementary facilities that provide researchers with state-of-the-art capabilities to fabricate, process, characterize and model nanoscale materials, and constitute the largest infrastructure investment of the National Nanotechnology Initiative. The NSRCs are located at DOE's Argonne, Brookhaven, Lawrence Berkeley, Oak Ridge, Sandia and Los Alamos National Laboratories. More information about the DOE NSRCs: science.energy.gov/bes/suf/user-facilities/nanoscale-science-research-centers
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
SIDEBAR: Beyond Lighting - InGaN in Action
The InGaN alloy is of extreme interest to scientists and inventors in the semiconductor and solid-state lighting fields. It has the ability to emit light over a wide range of wavelengths-manifesting as different colors-simply by changing the relative amounts of indium and gallium in the material. Scientists at the Center for Excitonics are exploring the fundamentals of light emission in this material, as well as pushing the frontiers of the exciting field of excitonics, where light and electrons interact both to store energy and mediate its transfer in a wide range of materials. In the case of InGaN alloys, this deeper understanding of excitonics can impact many real-world devices, including:
Blue and green light-emitting diodes (LEDs)
Ultra-high-efficiency solar photovoltaics
Green and blue diode lasers (e.g. laser pointers, Blu-ray writers)
High-power, high-voltage electronics
Phased radar arrays
Ultraviolet LEDs for medical and industrial applications
####
About Brookhaven National Laboratory
One of ten national laboratories overseen and primarily funded by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Brookhaven National Laboratory conducts research in the physical, biomedical, and environmental sciences, as well as in energy technologies and national security. Brookhaven Lab also builds and operates major scientific facilities available to university, industry and government researchers. Brookhaven is operated and managed for DOE's Office of Science by Brookhaven Science Associates, a limited-liability company founded by the Research Foundation for the State University of New York on behalf of Stony Brook University, the largest academic user of Laboratory facilities, and Battelle, a nonprofit applied science and technology organization.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Justin Eure
(631) 344-2347
or
Peter Genzer
(631) 344-3174
Copyright © Brookhaven National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








