Home > Press > Cold atoms for quantum technology
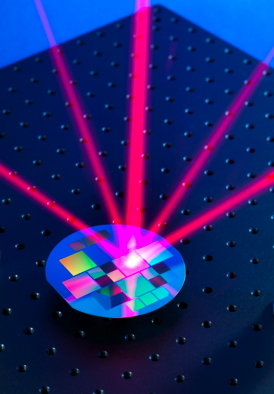 |
| A microfabricated grating transforms a single incoming laser beam into a light field specially tailored for trapping and cooling atoms |
Abstract:
Researchers from the National Physical Laboratory, University of Strathclyde, Imperial College London and University of Glasgow have developed a portable way to produce ultracold atoms for quantum technology and quantum information processing. Their research has been published in the journal Nature Nanotechnology, where it is featured on the front cover.
Cold atoms for quantum technology
Teddington, UK | Posted on May 12th, 2013Many of the most accurate measurement devices, including atomic clocks, work by observing how atoms transfer between individual quantum states. The longer the atomic transition can be observed, the more precisely it can be measured. Slow-moving ultracold atoms enable the longest observation times and the highest precision. By illuminating the atoms with laser light, the Doppler effect is used to cool them down to microkelvin temperatures, a task normally achieved in a large apparatus.
Complementary approaches to microfabricate the prototype chips were developed by NPL and Imperial College London. Following this, the team further developed the technology which can make an important contribution to metrology and high-precision measurements by enabling atomic quantum sensors to be miniaturised. Advanced versions of the specialised optical diffraction gratings were co-designed by the groups in the collaboration and microfabricated by Kelvin Nanotechnology Ltd using Glasgow's James Watt Nanofabrication Centre.
These researchers have developed a technology which enables a far more compact optical setup than previously, yet it can still cool and trap large numbers of atoms for use in portable instruments. They pattern the surface of a semiconductor chip to form a diffraction grating, splitting a laser into several beams that trap and cool the atoms.
Portable clocks, magnetometers and accelerometers have wide-ranging applications, including navigation on earth and in space, telecomunications, geological exploration, and medical imaging.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Alastair Sinclair
Tel:44 020 8943 6157
Copyright © National Physical Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Find out more about how laser cooling works:
Find out more about how laser cooling works:
![]() More on NPL's work on Quantum Detection:
More on NPL's work on Quantum Detection:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








