Home > Press > Boston College researchers' unique nanostructure produces novel 'plasmonic halos': Nanoscopic microcavities offer newfound control in light filtering
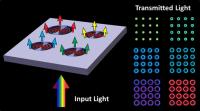 |
| Boston College researchers have constructed a unique nanostructure that exploits microcavity features to filter visible light into "plasmonic halos" of selected color output. The device could have applications in areas such as biomedical plasmonics or discrete optical filtering.
Credit: Nano Letters |
Abstract:
Using the geometric and material properties of a unique nanostructure, Boston College researchers have uncovered a novel photonic effect where surface plasmons interact with light to form "plasmonic halos" of selectable output color. The findings appear in the journal Nano Letters.
Boston College researchers' unique nanostructure produces novel 'plasmonic halos': Nanoscopic microcavities offer newfound control in light filtering
Chestnut Hill, MA | Posted on February 7th, 2013The novel nanostructure proved capable of manipulating electron waves known as surface plasmon polaritons, or SPPs, which were discovered in the 1950s but of late have garnered the attention of scientists for their potential applications in fields that include waveguiding, lasing, color filtering and printing.
The team put a layer of a polymer film on a glass substrate and then dotted the surface with holes precisely defined by a process of electron beam lithography, using the BC Integrated Sciences Nanofabrication Clean Room facility. The team next applied a layer of silver, thick enough to be nontransparent to visible light. In addition to covering the thin film on top, the silver coated the contours of the holes in the film, as well as the exposed circles of the glass substrate below. The effect produced an array of silver microcavities.
When the researchers directed light from below and through the glass substrate, light "leaking" through nanoscale gaps on the perimeters of the microcavities created SPP waves on their top surfaces. At particular wavelengths of the incident light, these waves formed modes or resonances analogous to acoustic waves on a drumhead, which in turn effectively filtered the light transmitted to the far side, accounting for the "halo" appearance, said Boston College Ferris Professor of Physics Michael Naughton, who co-authored the report with Senior Research Associate Michael J. Burns and doctoral student and lead author Fan Ye. The team's research was funded by the W. M. Keck Foundation.
Central to this control effect are "step gaps" formed along the perimeter of each circle, which give the nanostructure the ability to modulate which waves of light pass through. It is within this geometry that the interaction of light upon the silver surface coating resulted in the excitation of plasmon waves, said Naughton. Examination of the SPPs by Mr. Ye using a near-field scanning optical microscope offered unique insights into the physics at work within the structure, Naughton said.
By adjusting the type of metal used to coat the structure or varying the circumferences of the microcavities, Naughton said the step-gap structure is capable of manipulating the optical properties of the device in the visible light range, giving the researchers newfound control in light filtering.
This kind of control, the team reports, could have applications in areas such as biomedical plasmonics or discrete optical filtering.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ed Hayward
617-552-4826
Copyright © Boston College
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Thin films
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








