Home > Press > New information on binding gold particles over metal oxide surfaces
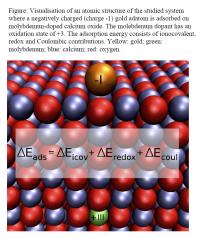 |
| This is a visualization of an atomic structure of the studied system where a negatively charged (charge -1) gold adatom is adsorbed on molybdemun-doped calcium oxide. The molebdenum dopant has an oxidation state of +3. The adsorption energy consists of ionocovalent, redox and Coulombic contributions. Yellow: gold; green: molybdenum; blue: calcium; red: oxygen.
Credit: Karoliina Honkala |
Abstract:
The strong binding of gold on electronically modified calcium oxide can now be understood in detail. In a computational study, researchers Jenni Andersin, Janne Nevalaita, Karoliina Honkala and Hannu Häkkinen at the University of Jyväskylä Nanoscience Center have shown how redox chemistry entirely determines the adsorption strength of gold on the modified oxide where one metal atom is replaced with molybdenum. The study was funded by the Academy of Finland.
New information on binding gold particles over metal oxide surfaces
Finland | Posted on January 22nd, 2013The research team applied the so-called Born-Haber cycle to analyse how different terms contribute to adsorption energy. The calculations were done at the supercomputers of the CSC - IT Center of Science by employing quantum mechanical simulation methods.
In the oxide lattice, the molybdenum atom donates two electrons into the oxide. When a gold atom adsorbs on the oxide surface, a redox reaction takes place. In this process, a third electron transferred by the dopant is gained by gold, and energy is released. By varying the dopant among several transition metal atoms, the researchers found that the amount of energy released linearly correlates with the ability of the dopant to give an electron. The trend can be used to estimate how much a guest atom stabilises gold adsorption without calculating the adsorption energy.
The research results are important for understanding catalyst-support interaction. The results fully support the experimental observation where gold nanoparticles have been seen to form flat structures over modified calcium oxide surfaces. A similar Born-Haber cycle, as applied in this study, can also be employed to analyse oxide-catalysed chemical reactions that follow the redox mechanism.
Catalysts are commonly used by industry, for instance, in the production of fuels, plastics, fertilisers and other similar products. Metal oxide surfaces are widely used as support materials for metal catalysts particles. The binding properties and shape of metal nanoparticles sensitively depend on the interaction between the support and the catalyst. By tuning this interaction, it is possible to affect the number and properties of catalytically active sites, or even create new sites. One way to modify the interaction is to dope the oxide with guest metal atoms that can donate extra electrons into a material.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Docent Karoliina Honkala
University of Jyväskylä
Department of Chemistry
Nanoscience Center
358-408-053-686
Academy of Finland Communications
Communications Specialist
Leena Vähäkylä
tel. +358 29 533 5139
firstname.lastname(at)aka.fi
Copyright © Academy of Finland
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








